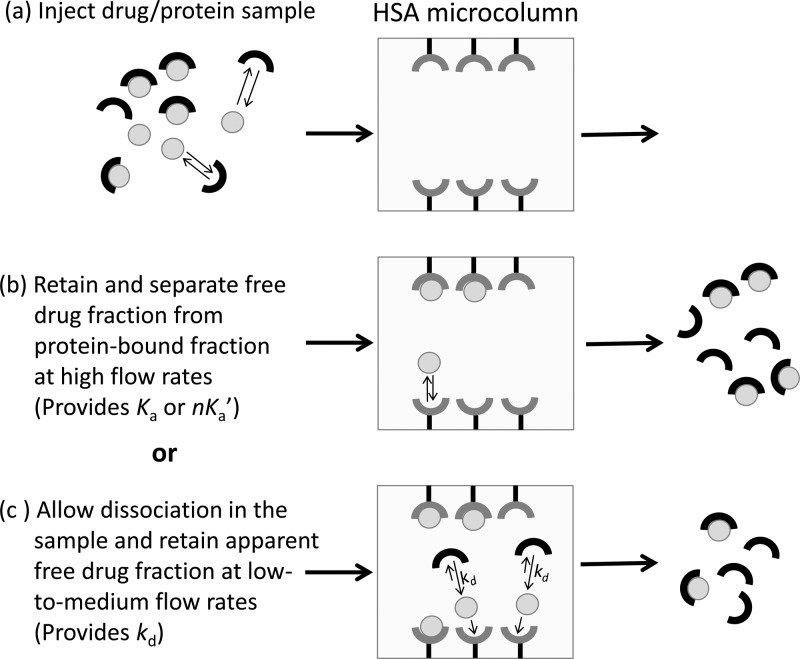
Figure 1.
General scheme for measuring a free drug fraction by ultrafast affinity extraction. (a) A sample containing a drug/protein mixture is injected onto an affinity microcolumn that contains an immobilized binding agent for the drug, such as HSA. (b) As the sample passes through the microcolumn at a suitably high flow rate, only the free drug fraction will be extracted; this creates a separation of the free and protein-bound forms of the drug in the sample and provides data that can be used to estimate the association equilibrium constant (Ka) or global affinity constant (nKa′) for the interaction. (c) If a slower flow rate is used for sample injection, part of the protein-bound fraction of the drug in the sample may dissociate as it passes through the microcolumn, increasing the apparent free drug fraction; these conditions provide data that can be used to estimate the dissociation rate constant (kd) for the system.