Figure 1.
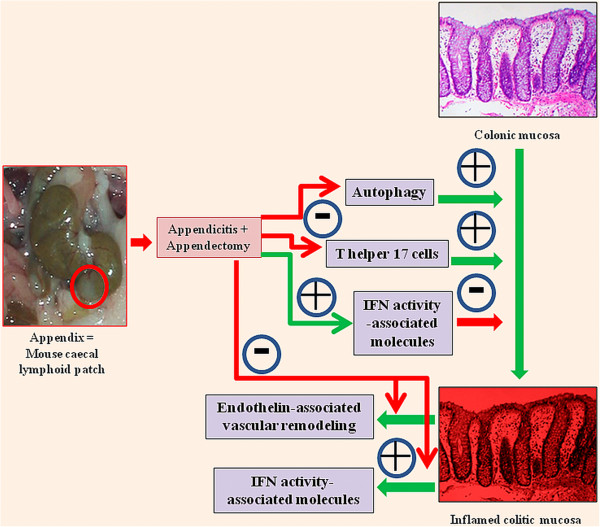
Biological markers of inflammation and immunity correlating with our murine model of appendicitis (and appendectomy) [24],[25]. Appendicitis and appendectomy performed in the most proximal colon induce gene expression changes to curb T helper 17 cell activities, curtail autophagy, modulate interferon activity-associated molecules, and suppress endothelin vasoactivity-mediated immunopathology/vascular remodelling in the most distal colon. These contribute to the limitation/amelioration of colitis pathology.
