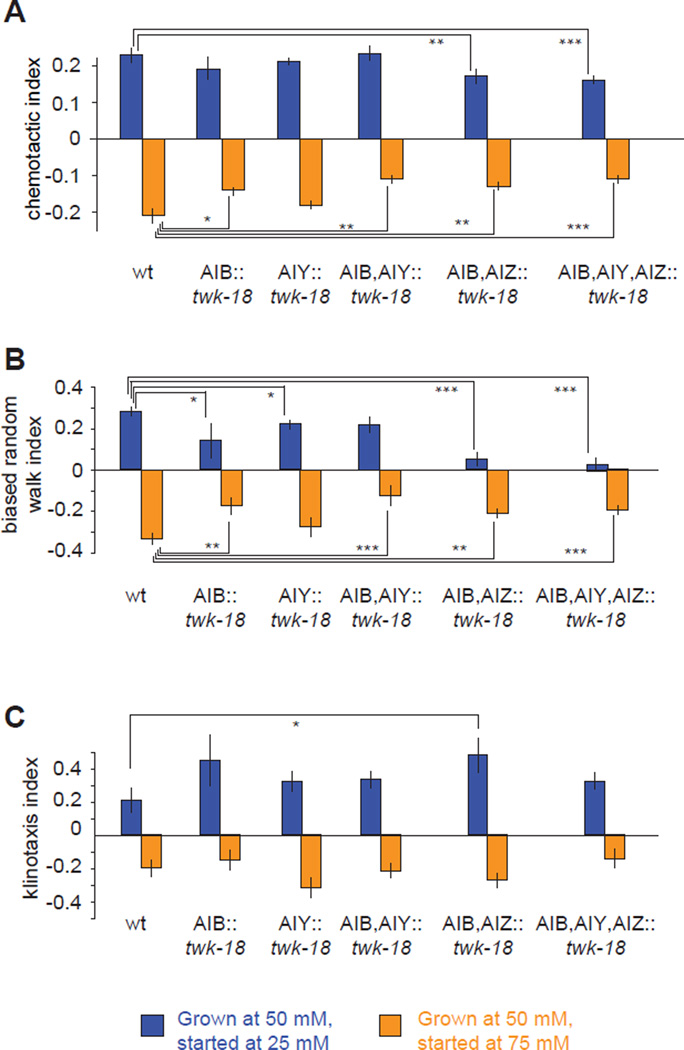
Figure 7. Downstream interneurons differentially regulate the biased random walk and klinotaxis.
A–C) Chemotactic index (A), biased random walk index (B) and klinotaxis index (C) for wild-type and transgenic animals in which different interneurons are inhibited by ectopic expression of a constitutively active potassium channel twk-18(gf). The biased random walk index was calculated as the fractional difference in the relative run durations up or down gradients (〈rup〉 − 〈rdown〉)/(〈rup〉 + 〈rdown〉) based on the trajectories of individual animals (see Figure 2B and 2D). The klinotaxis index was calculated as the fractional difference in the relative probabilities of sharp turns reorienting the animal up or down the gradient (〈pup〉 − 〈pdown〉)/(〈pup〉 + 〈pdown〉) as calculated based on the trajectories of individual animals (see Figure 2C and 2E). Significant differences between salient comparisons were calculated using ANOVA Tukey-Kramer post hoc, *** p<0.0005; ** p<0.005, * p<0.05, n >60 animals for each measurement. Data points represent mean ± SEM.