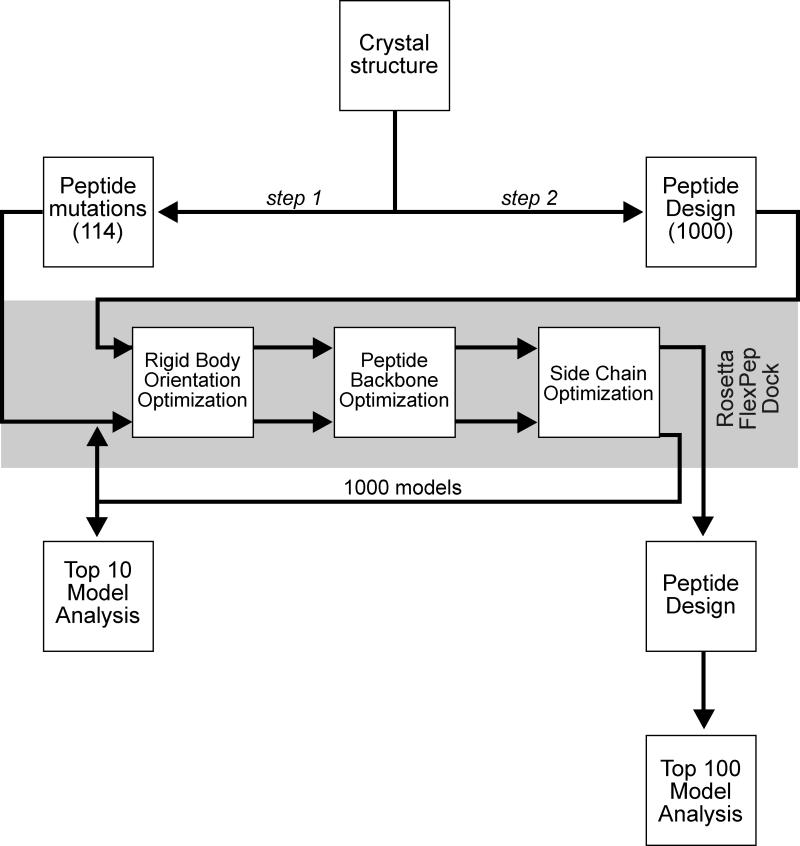
Figure 2. Scheme utilized in our modeling study.
Step 1: The GRFQVT peptide complexed in WNK4 was initially removed from the crystal structure (2v3s) and docked back into the hydrophobic pocket of the OSR1 CCT/PF2 domain along with 114 hexapeptide variants (point mutations at every position with the other 19 canonical amino acid residues). One thousand models were created using Rosetta FlexPepDock for each peptide and the top 10 models from each of the 1000 runs were averaged for analysis. Step 2: The Rosetta design application was used to produce 1000 whole hexapeptide mutants based on binding of the individual residues of the wild-type hexapeptide to the CCT/PF2 domain. FlexPepDock was then employed and binding energies of the complexes were calculated. The top 100 models were analyzed.