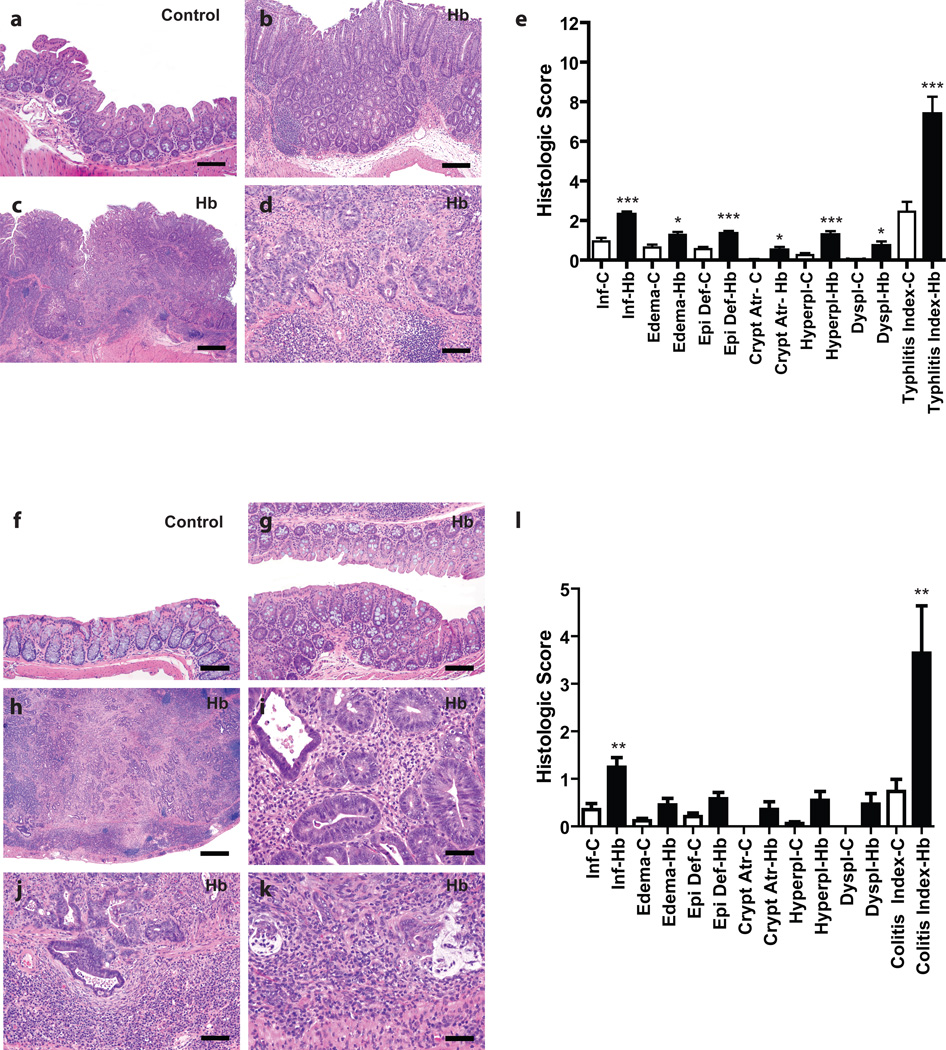
Figure 4. Rederived Helicobacter spp.-free WKO mice infected with H. bilis develop typhlitis and colitis at 7–9 months post infection.
(a) Representative cecum from an uninfected control mouse at 7 mpi with sparse inflammatory cells in the lamina propria and lack of other significant epithelial changes (bar = 80 µM). (b) Representative non-neoplastic cecum of a H. bilis-infected mouse at 7 mpi showing moderate mucosal and submucosal inflammation, edema, surface epithelial tethering, epithelial hyperplasia and minimal dysplasia (bar = 160 µM). (c) Low magnification image of the cecum of a H. bilis-infected male at 7 mpi that developed a broad-based mucosal proliferative lesion (diagnosed as intramucosal carcinoma) showing prominent inflammation, edema, epithelial defects, epithelial hyperplasia, and disorganized glandular architecture (bar = 400 µM). (d) Higher magnification view of (c) showing high-grade dysplastic glands with invasion into the muscularis mucosa and extension/herniation into the submucosa (bar = 80 µM). (e) Mean subscores ± SEM of inflammation (inf), edema, epithelial defect (epi def), crypt atrophy (crypt atr), hyperplasia (hyperpl), dysplasia (dyspl), contribute to the cumulative typhlitis index of all mice. (f) Representative H&E image of the colon from an uninfected control mouse at 7 mpi with no significant mucosal inflammation or other epithelial alterations (bar = 80 µM). (g) Representative image of a non-neoplastic colon from an H. bilis-infected at 7 mpi showing mild mucosal inflammation and minimal hyperplasia (bar = 80µM). (h) Low magnification H&E image of a grossly thickened colon from a H. bilis-infected male at 7 mpi showing severe transmural mixed inflammation, lympho-follicular formation, edema, epithelial defects, fibrosis, crypt loss, marked epithelial hyperplasia, and severely disorganized glandular architecture with high grade dysplasia and multifocal submucosal invasion/herniation (bar = 400 µM). (i) Higher magnification view of (h) showing dysplastic glands with frequent mitotic activity and luminal cellular debris in a background of granulocytic inflammation (bar = 40µM). (j) Higher magnification of (h) showing invasive high grade dysplastic/neoplastic glands in the muscularis mucosa and submucosa surrounded by proliferating fibroblasts and dense lympho-plasmacytic inflammation (bar = 80µM). (k) Higher magnification of (h) showing a focus of invasive glands deep in the submucosa with associated partial loss of epithelial lining, disorganized pools of mucin-like material, and associated dense inflammatory cellular aggregates (bar = 40µM). (l) Subscores contributing to the colitis total index of all mice. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.005 on Mann-Whitney test comparing un-infected and infected mice in that subscore. C = uninfected control mice; Hb = H. bilis-infected mice; mpi = months post infection.