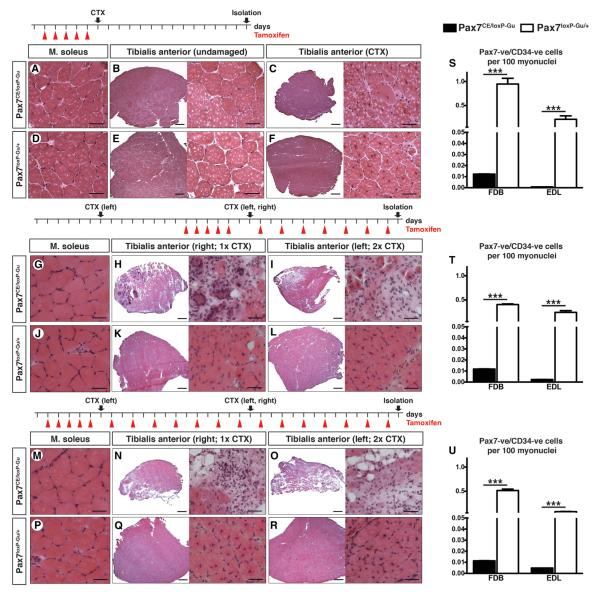
Figure 2. Impaired Muscle Regeneration in Adult Mice after Enhanced Inactivation of Pax7.
(A–F, G–L, and M–R) Morphological analysis of T.A. muscles of TAM-treated Pax7CE/loxP-Gu and Pax7loxP-Gu/+ mice injected with CTX to induce muscle regeneration. TAM treatment regimens and time points of analysis are indicated at the top of each panel. (A–F) HE staining of T.A. muscles of 12-week-old mice (n = 3) 14 days after CTX injection. Cre-recombinase-mediated inactivation of Pax7 was induced by five consecutive TAM injections. (G–R) HE staining of T.A. muscles of 20-week-old mice (n = 3), which received additional administration of TAM after one (H and K) or two (I and L) rounds of muscle regeneration. TAM was administered before and during the first round of muscle regeneration (G and L) or before and during two rounds of muscle regeneration (M–R). (S–U) Number of Pax7-positive and CD34-positive SC populations on isolated myofibers relative to the number of myonuclei (DAPI). Error bars represent standard deviation of the mean (t test: ***p < 0.001). Scale bar: overview = 200 μm; magnification = 25 μm. See also Figure S3.