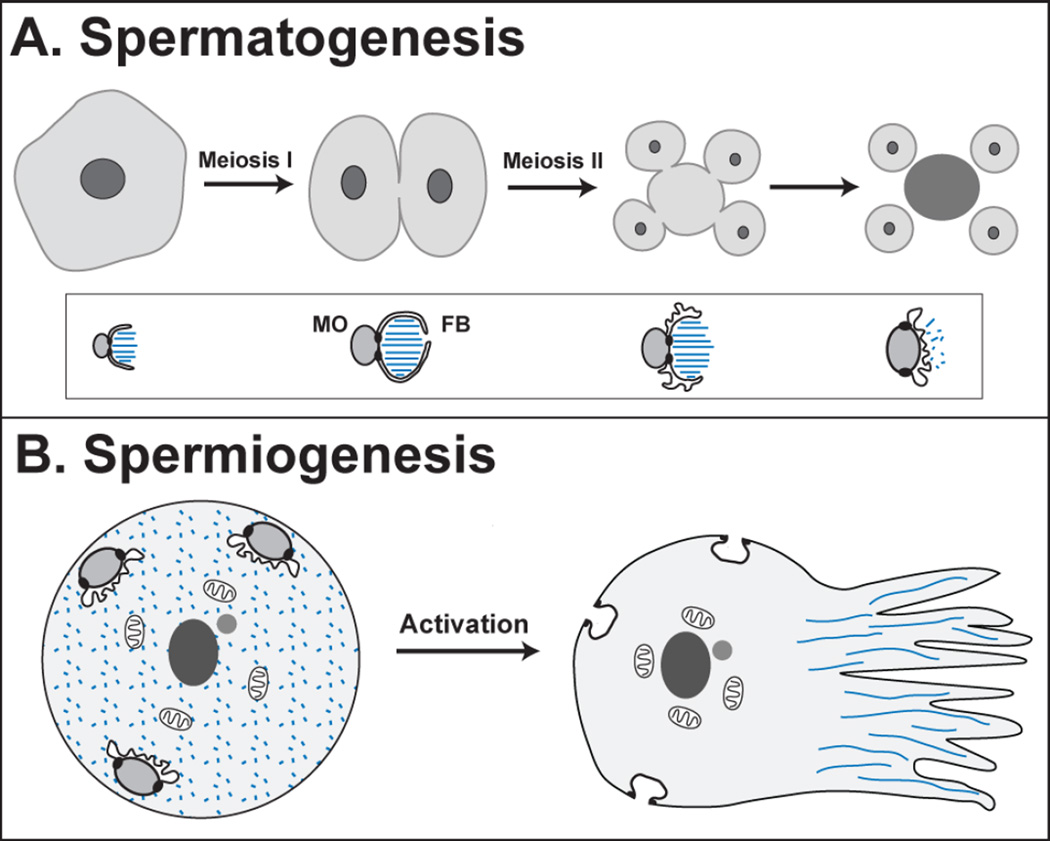
Figure 2. Spermatogenesis and Spermiogenesis.
(A) During spermatogenesis, the primary spermatocyte undergoes two meiotic divisions, producing four spermatids (light gray) and a residual body (dark gray). The pattern of cytokinesis sometimes varies [55]. During this process, the membranous organelles (MOs) localize many sperm proteins, and their associated fibrous bodies (FBs) are made of polymerized major sperm protein (MSP, blue) until its release and depolymerization in the mature spermatid. The differentiation of these organelles is shown in the inset below each stage. (B) During spermiogenesis, a spermatid activates to become a motile sperm. The MOs fuse with the plasma membrane in the head of the sperm, and the MSP forms polymers that organize the pseudopod.