Figure 1.
MBD3 Facilitates the Initiation of Reprogramming
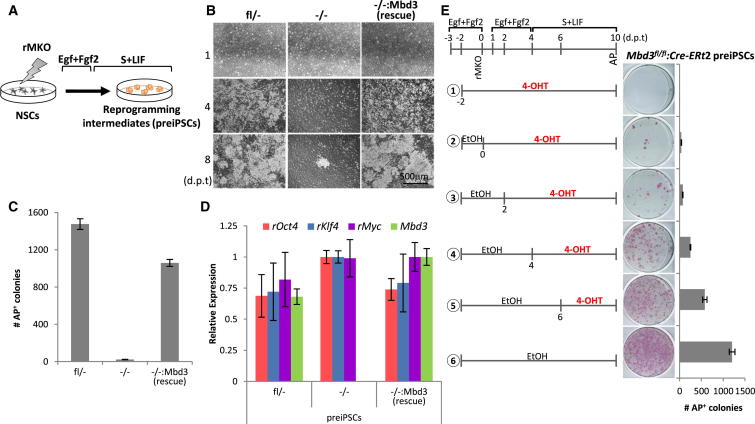
(A) Experimental design used to address the kinetics and efficiency of initiation of reprogramming in NSCs with different Mbd3 genotypes. NSCs were transduced with retroviruses encoding cMyc, Klf4, and Oct4 (rMKO), maintained in Egf+Fgf2 medium for 3 days, and then switched to S+LIF medium.
(B) Phase images of the reprogramming intermediates (preiPSCs) emerging from Mbd3fl/−, Mbd3−/−, and Mbd3−/−:Mbd3 (rescue) NSCs at different days posttransduction (d.p.t.).
(C) Efficiency of preiPSC colony formation per 2.5 × 105 NSCs as assessed by alkaline phosphatase (AP) staining at day 9 posttransduction.
(D) qRT-PCR analysis of retroviral transgenes (rOct4, rKlf4, and rMyc) and Mbd3 expression in the obtained preiPSCs maintained in S+LIF. Three independent NSCs transductions were carried out and gene expression was assessed 12 days after transduction. Values are normalized to Gapdh value and shown as relative to the highest value.
(E) Time course of MBD3 requirement during preiPSC formation. Mbd3fl/fl NSCs were stably transfected with pCAG-CreERt2 transgene, transduced with retroviral transgenes, and treated with 4-OHT at indicated time points to induce Cre-mediated deletion of the floxed alleles during reprogramming. Ethanol (EtOH) was used as a control. The encircled numbers correspond to different conditions. PreiPSC colony formation was assessed by AP staining at day 10 posttransduction and is presented as the number of colonies per 7.5 × 104 NSCs. The error bars indicate STDEV.