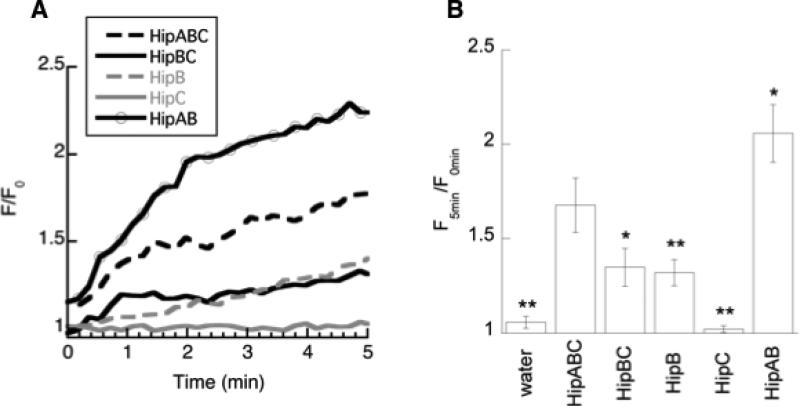
Figure 2.
Membrane permeabilization in E. coli caused by the addition of peptides measured using a propidium iodide uptake assay. A) Representative data for peptides considered in this study. Data is plotted as fluorescence at a given time after peptide addition relative to the average fluorescence in the minute before peptide was added (F/F0). B) Permeabilization results averaged over multiple trials, reported as a ratio of the fluorescence five minutes after peptide addition divided by the fluorescence averaged for the minute before peptide was added. Average of at least three trials is shown with variation provided as standard error. Measurements that were significantly different from HipABC at the p<0.10 (*) and p<0.05 (**) level are denoted with asterisk.