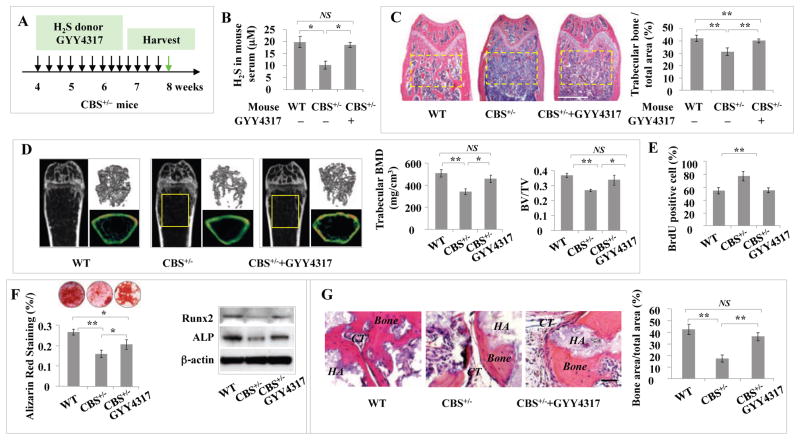
Figure 4. Intraperitoneal injection of H2S donor GYY4317 rescued osteopenia phenotype and BMMSC function in CBS+/− mice.
(A) H2S donor GYY4317 was IP injected to CBS+/− mice every other day at 1 mg/mouse for 28 days (total 14 times). After the last injection, the samples were harvested for further experiments. (B–D) After GYY4317 treatment, CBS+/− mice showed significantly increased serum H2S levels (B), femur trabecular bone volume as shown by H&E staining (C), bone mineral density (BMD) and bone volume/tissue volume (BV/TV) as shown by microQCT (D). Wildtype mice were used as control (WT). (E–G) When compared with CBS+/− BMMSCs (CBS+/−), BMMSCs from GYY4317-treated CBS+/− mice (CBS+/− +GYY4317) showed reduced proliferation as evaluated by BrdU labeling (E), elevated mineralized nodule formation shown by alizarin red staining, elevated expression of ostegenic markers Runx2 and ALP (F), and increased new bone formation when implanted into immunocompromised mice subcutaneously using HA/TCP as a carrier (HA). CT: connective tissue (G). Wildtype mice were used as control (WT). * P<0.05, ** P< 0.01, scale bar: 1000 μm (C), 200 μm (H). Experiments were repeated three times. See also Figure S4.