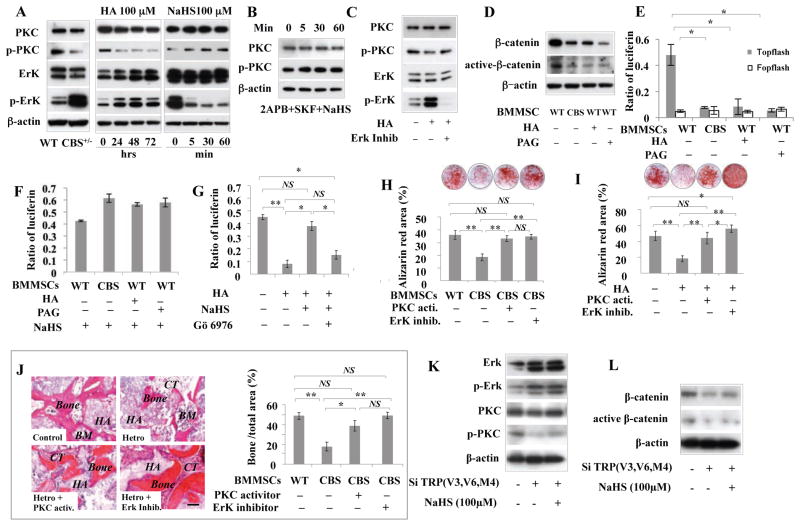
Figure 7. H2S-deficiency downregulated Wnt/β-catenin pathway via reduced Ca2+ influx in BMMSCs.
(A) CBS+/− and H2S inhibitor HA (100 μM)-treated BMMSCs cultured for 24, 48, or 72 hours showed significant downregulation of p-PKC and upregulation of p-Erk. In contrast, H2S donor NaHS (100 μM) treatment for 5, 30, or 60 minutes upregulated p-PKC and downregulated p-Erk in BMMSCs. (B) When pretreated with 2APB (10 μM) and SKF-96365 (10 μM) for 15 min to block Ca2+ influx, NaHS treatment failed to upregulate p-PKC expression in BMMSCs. (C) Erk inhibitor (PD325901 1 μM) treatment failed to affect p-PKC expression in BMMSCs, indicating that Erk might be the downstream the PKC signaling. (D) When CBS inhibitor HA (100 μM) or CSE inhibitor PAG (100 μM) was used to reduce H2S levels, BMMSCs showed significant reduction in total β-catenin and active β-catenin expression at 3 days post-treatment. (E) When TOPflash and control FOPflash were transfected into normal and CBS+/− BMMSCs, luciferase activity indicated that the canonical Wnt/β-catenin pathway was inhibited in CBS+/− BMMSCs in comparison to normal BMMSCs. (F) Reduced β-catenin expression in both CBS+/− and H2S inhibitor HA (100 μM)-treated BMMSCs was rescued by H2S donor NaHS (100 μM) treatment, as assessed by luciferase activity. (G) Rescue of β-catenin expression by NaHS (100 μM) in both CBS+/− and HA (100 μM)-treated BMMSCs was blocked by PKC inhibitor (Gö 6976, 10 nM) treatment, as assessed by luciferase activity. (H, I) PKC activator and Erk inhibitor treatment rescued the osteogenic deficiency in both CBS+/− and HA-treated BMMSCs, as assessed by alizarin red staining to show mineral nodule formation. (J) In vivo BMMSC implantation showed that PKC activator and Erk inhibitor treatment rescued CBS+/− BMMSC-mediated new bone formation. HA: HA/TCP; BM: bone marrow; CT: connective tissue. (K) Western blotting showed that combinative knockdown of TRPV6, TRPV3, and TRPM4 channels by siRNA led to upregulation of p-Erk and downregulation of p-PKC, active-β-catenin and β-catenin. (L) H2S donor NaHS treatment failed to rescue the altered expression of p-Erk, p-PKC, active-β-catenin and β-catenin, as assessed by Western blotting. * P<0.05, ** P< 0.01. Experiments were repeated three times. See also Figure S7.