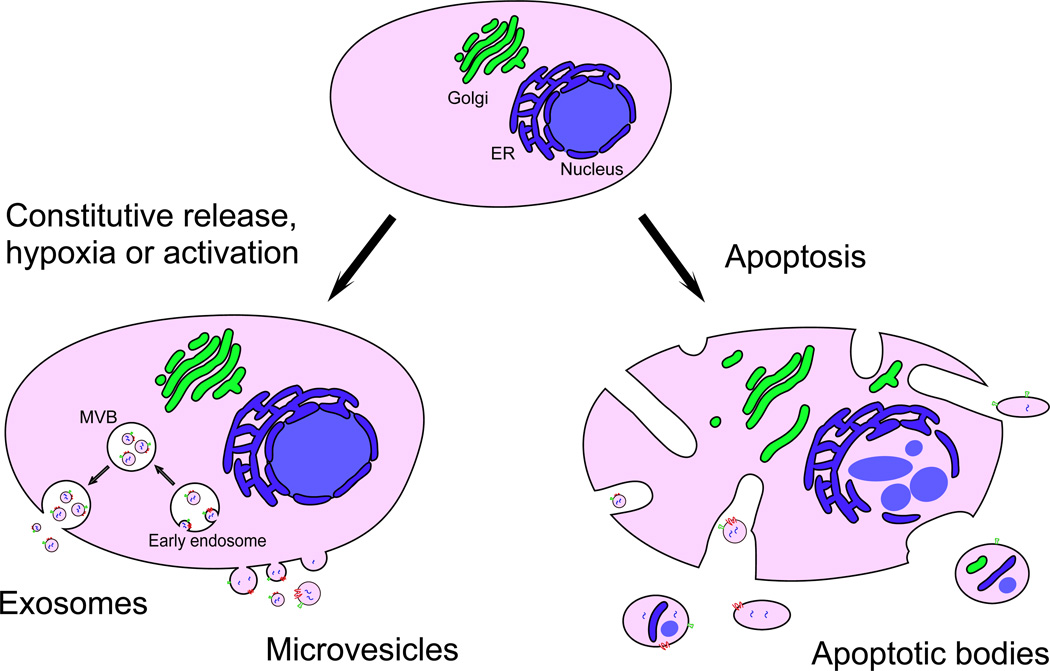
Figure 1. Types of EVs released by tumour cells.
Exosomes and microvesicles are released constitutively and/or upon activation. Exosomes are formed from endosomes through inward budding to generate multivesicular bodies (MVBs) and are released upon fusion of MVBs with the plasma membrane. Exosomes are relatively homogeneous in size and, because of their endocytic origin, contain proteins involved in endosomal-lysosomal sorting which are used as exosomal markers. Microvesicles on the other hand are formed through direct outward budding of the plasma membrane. Tumour cells undergoing apoptosis release apoptotic bodies, which are formed by random blebbing of the plasma membrane. Apoptotic bodies are heterogeneous in size and may contain nuclear fragments as well as fragments of cytoplasmic organelles. Abbreviations: ER, endoplasmic reticulum; MVB, multivesicular body.