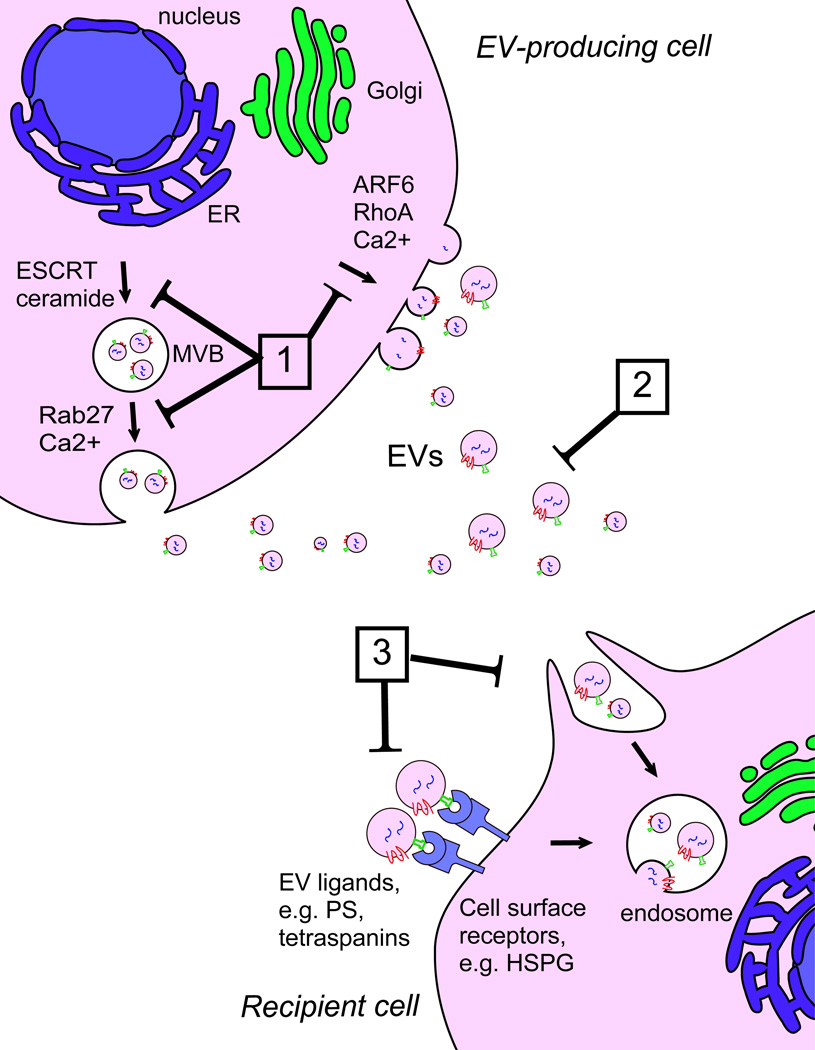
Figure 3. Therapeutic targeting of EV signalling in cancer.
Different potential strategies to interfere with EV-mediated intercellular communication can be envisioned. (1) Inhibition of EV biogenesis or release through interference with components of pathways involved in EV formation (e.g. ESCRT, ceramide) or release (e.g. Rab27, ARF6, RhoA). (2) EV removal from the circulation by extracorporeal hemofiltration. (3) Inhibition of EV uptake in recipient cells by blocking EV ligands (e.g. PS, tetraspanins) or cell surface receptors involved in EV binding or internalization (e.g. HSPGs). Abbreviations: ARF6, ADP-ribosylation factor 6; Ca, calcium; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; ESCRT, Endosomal Sorting Complex Required for Transport; HSPG, heparan sulfate proteoglycans; MVB, multivesicular body; PS, phosphatidylserine; RhoA, Ras homolog family member A.