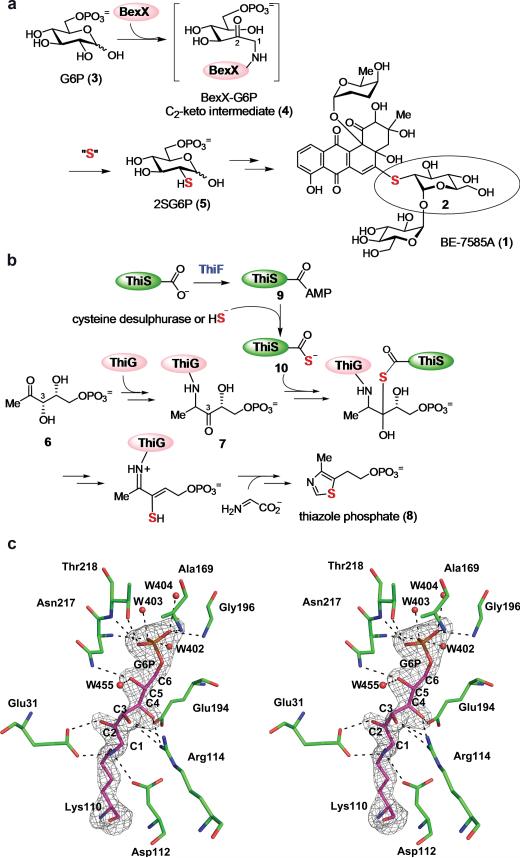
Figure 1. Proposed mechanism for 2-thiosugar formation in BE-7585A biosynthesis.
a, Proposed BexX-catalyzed 2-thiosugar formation. The active site lysine residue (K110)6,7 of BexX initially forms an imine bond with G6P (3) at the C1 position, which is isomerized first to a C1–C2 enamine and then a C2-ketone intermediate (4). Subsequent nucleophilic attack by a sulphur donor occurs at the C2 position of 4 to incorporate a sulphur atom in the 2SG6P (5) product. b, ThiG-catalyzed thiazole phosphate biosynthetic pathway. c, Stereo diagram of BexX active site. Active site side chains and Lys110-G6P intermediate are depicted as sticks with the carbon atoms of residues colored in green and purple, respectively. The Fo-Fc simulated annealing (SA)-omit map of Lys110-G6P intermediate contoured at 4 sigma is shown in gray. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. The carbon atoms of G6P are numbered from C1 to C6.