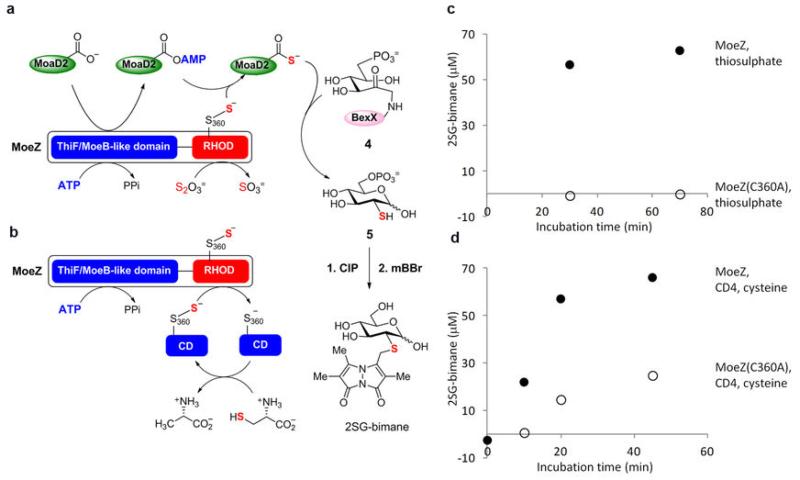
Extended Data Fig. 9. BexX-catalyzed 2-thiosugar formation using various sulphur sources.
a, b, Reaction scheme of C-His6-BexX-catalyzed 2-thiosugar formation utilizing NHis6-AoMoeZ, N-His6-AoMoaD2 and (a) thiosulphate or (b) L-cysteine and cysteine desulphurase (CD4) from A. orientalis. The reactions were carried out in the absence of reducing agent to avoid complications from generation of bisulphide from protein persulphide (see also below*). Under this condition, AoMoeZ cannot be regenerated after single-turnover. The thiosugar product was derivatized with mBBr and then treated with alkaline phosphatase (CIP) to yield 2-thio-D-glucose-bimane (2SG-bimane). c, d, The 2SG-bimane product concentrations in different incubation time points with (c) thiosulphate or (d) L-cysteine and CD4 as the sulphur source were estimated based on the product peak area of each HPLC trace. The 2SG-bimane synthetic standard (10, 25, 50, 77, 100, 200 μM) was used for the calibration. The closed and open circles denote product formation from the incubation with N-His6-AoMoeZ and N-His6-AoMoeZ(C360A) mutant, respectively. *The observed minor product formation with MoeZ(C360A) mutant, L-cysteine and CD4 (see d, open circles) is likely caused by the formation of bisulphide, which could be generated upon reduction of CD4-persulphide in the presence of free cysteine molecules. In fact, small amount of bisulphide could be detected under similar conditions with L-cysteine and CD4 (in the absence of other proteins and reducing agents) within 15-min incubation by the methylene blue assay45.