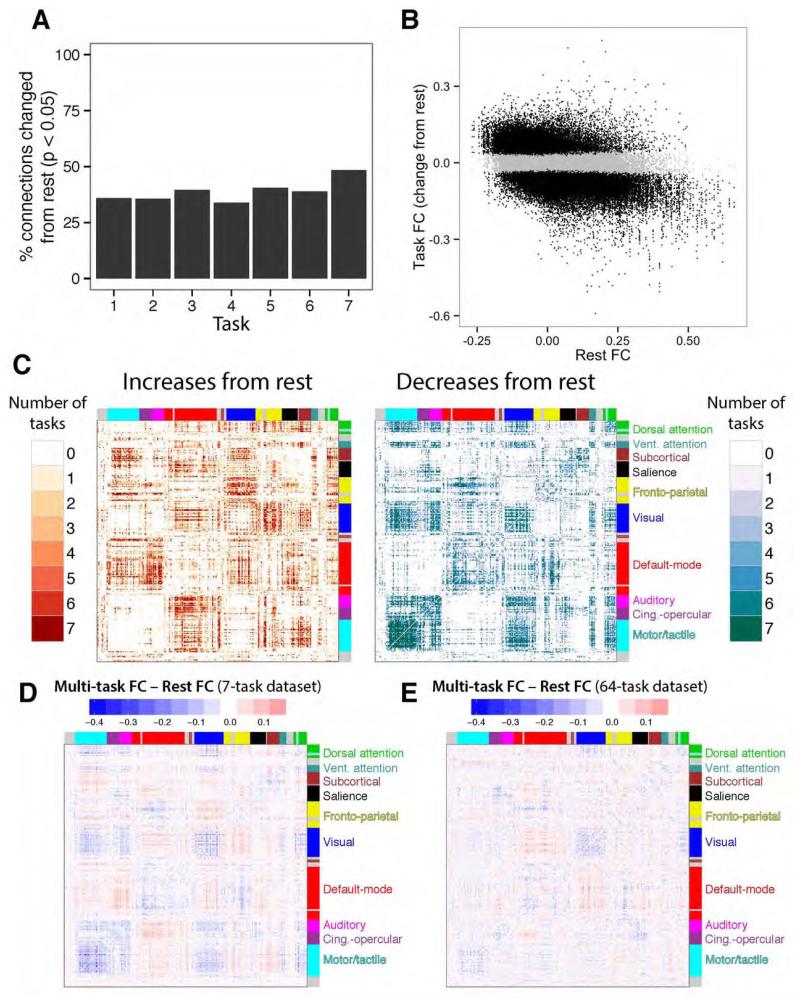
Figure 8. Task-evoked FC changes from rest reveal a task-general dynamic network architecture.
A, Each task’s whole-brain FC matrix was compared to the resting-state FC matrix (from Figure 4). The task order is the same as in Figure 1B. B, All task FC changes from rest are plotted (across all seven tasks) versus their resting-state FC values. Significant changes from rest are black, while non-significant changes are grey. Most of the connections (61%) were non-significant. The correlation between task FC changes and rest FC was negative for all seven tasks (mean r=−0.49). C, The count of how many tasks involved significant changes from rest plotted for each connection. Many connections changed for all seven tasks (11% of changed connections). D, Differences between the multi-task FC matrix and resting-state FC matrix (left vs. right sides of Figure 4), summarizing general changes from rest that are common across tasks. E, The same analysis for the 64-task dataset, on the same scale as panel D. The matrices in D and E were relatively similar (despite major differences between datasets): r=0.31, p<0.00001.