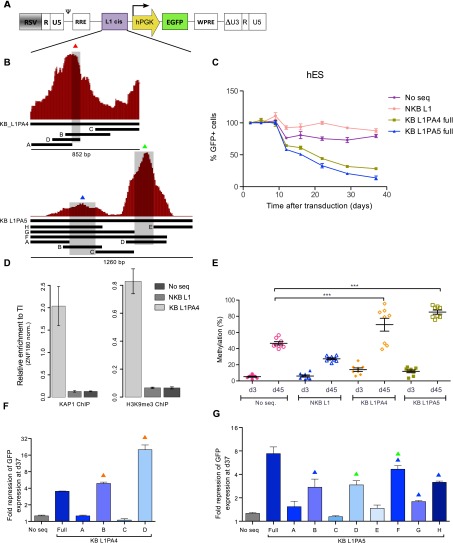
Figure 2.
KAP1-binding L1 fragments can induce repression and DNA methylation of a heterologous promoter in hES. (A) KB (KB L1PA4 and KB L1PA5) and NKB (NKB L1PA4) L1 sequences were cloned in depicted lentiviral vector upstream of a PGK-EGFP expression cassette. The resulting vectors were transduced in hES, and EGFP expression was monitored over time by FACS. (B) Schematic representation of the KAP1 ChIP peaks mapped on the L1PA4 and L1PA5 5′ end, with indication of derived fragments and subfragments cloned in the vector depicted in A. (C) Monitoring of GFP expression in hES cells transduced with the indicated vectors. (No seq) Lentiviral vector with no ERE-derived fragment upstream of the expression cassette. The figure shows the mean and SD of two biological replicates. (D) KAP1 and H3K9me3 recruitment to indicated lentiviral vectors in hES, assessed 35 d after transduction by ChIP-qPCR using PGK-specific primers. The figure illustrates the mean and SD of technical replicates. This experiment was performed twice with similar results (see Supplemental Fig. S3). Relative enrichment was determined by normalizing to a known positive (ZNF180 3′ UTR) control. (E) Influence of the L1 cis-acting sequences on the methylation of the nearby PGK promoter. Methylation of eight CpG positions was evaluated by pyrosequencing at days 4 and 35 after transduction of hES cells with the PGK-GFP lentiviral vectors. Mean and standard error mean (SEM) of two biological replicates is shown. Statistical differences were determined by one-way ANOVA test using the Bonferroni multiple test adjustment. (***) P ≤ 0.001. (F,G) Fold repression of the indicated vectors containing L1 subfragments described in B, assessed 37 d after transduction (respect to day 5). Overtime fold repression is presented in Supplemental Figure S3. Colored triangles indicate the presence of L1 sequences overlapping with the summits of the respective KAP1 ChIP-seq peaks as depicted in B.