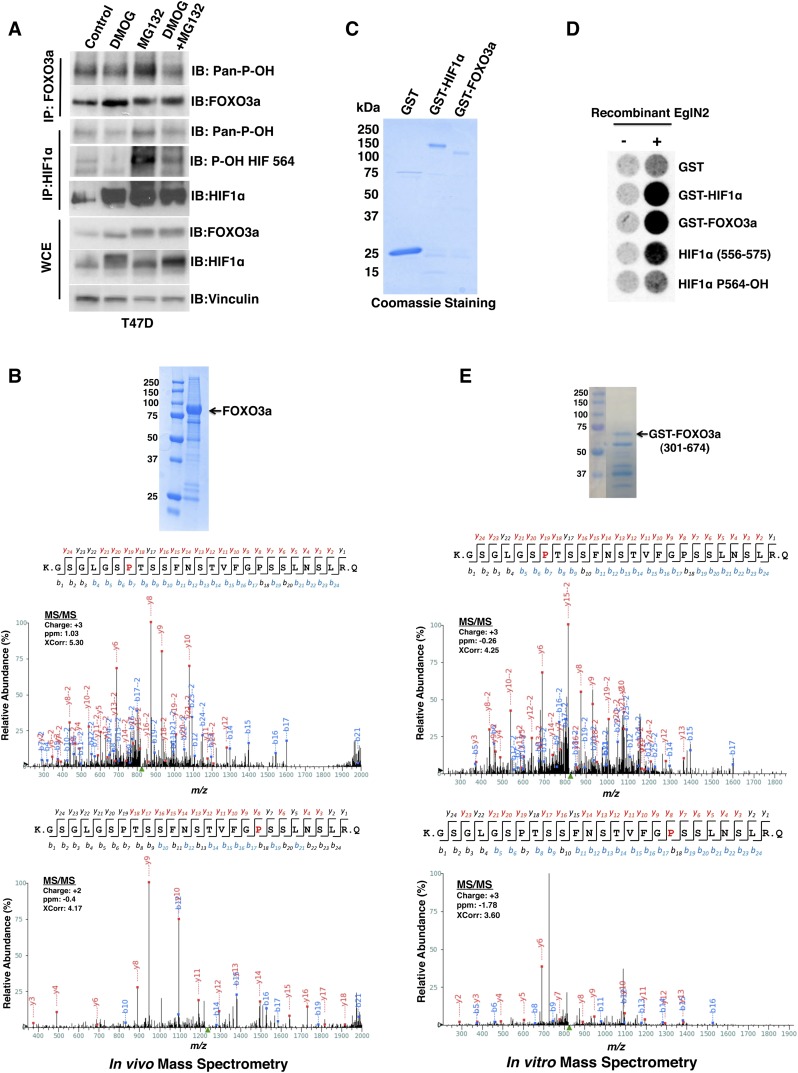
Figure 2.
EglN2 prolyl hydroxylates FOXO3a in vivo and in vitro. (A) Immunoblot (IB) assays of whole-cell extracts (WCEs) and immunoprecipitates (IPs) of T47D cells treated with either vehicle control, 1 mM DMOG, 10 μM MG132, or both 1 mM DMOG and 10 μM MG132. (B) 293FT cells were cotransfected to produce HA-FOXO3a and Flag-EglN2 and then treated with MG132. (Inset) HA-FOXO3a was purified by anti-HA immunoprecipitation followed by SDS–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and Coomassie blue staining. Shown are liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) data for the excised FOXO3a band corresponding to FOXO3a peptides hydroxylated at Pro426 or Pro437. The red “P” indicates a hydroxylated proline residue. (C,D) Coomassie blue staining (C) and in vitro hydroxylation assays (D) with the indicated GST fusion proteins. Synthetic HIF1α peptides corresponding to residues 556–575 were included as controls in D. P564-OH indicates 556–575 peptide hydroxylated at Pro564. (E) GST-FOXO3a (301–674) was incubated with recombinant EglN2, resolved by SDS–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and stained with Coomassie blue. Shown are MS/MS data for the excised FOXO3a band corresponding to FOXO3a peptides hydroxylated at Pro426 or Pro437. The red “P” indicates a hydroxylated proline residue. The peak heights are the relative abundances of the corresponding fragment ions, with the annotation of the identified matched N terminus-containing ions (b ions) in blue and C terminus-containing ions (y ions) in red.