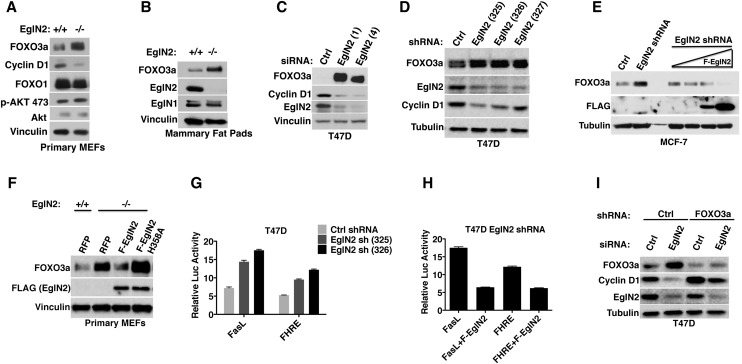
Figure 3.
FOXO3a protein abundance is regulated by EglN2 and links EglN2 to Cyclin D1. (A,B) Immunoblot analysis of primary MEFs (A) and mammary fat pads (B) derived from EglN2+/+ and EglN2−/− littermates. (C,D) Immunoblot analysis of T47D cells after transfection with EglN2 siRNA (C) or infection with lentiviruses encoding EglN2 shRNAs. Unrelated nontargeting siRNA and shRNA sequences were used as controls (Ctrl). (E) Immunoblot analysis of MCF-7 cells that were infected with a lentivirus encoding EglN2 shRNA or Ctrl shRNA and, after drug selection, superinfected with a lentivirus encoding Flag-EglN2 (F-EglN2) under the control of a doxycycline-inducible promoter. Increasing amounts of doxycycline were added to the cells 48 h before lysis as indicated by the triangle. (F) Immunoblot analysis of primary MEF cells that were infected with a lentivirus encoding red fluorescent protein (RFP) or Flag-tagged EglN2 (wild-type or H358A). (G,H) Luciferase reporter assay of T47D cells that were infected with a lentivirus encoding EglN2 shRNA (325 or 326) or Control (Ctrl) shRNA followed by transfection with either FasL or FHRE reporter plasmid in the absence or presence of shRNA-resistant Flag-EglN2 (F-EglN2) with TK-Renilla as an internal control. (I) Immunoblot analysis of T47D cells that were infected with a lentivirus encoding FOXO3a shRNA or control (Ctrl) shRNA and then transfected with either EglN2 siRNA or Ctrl siRNA.