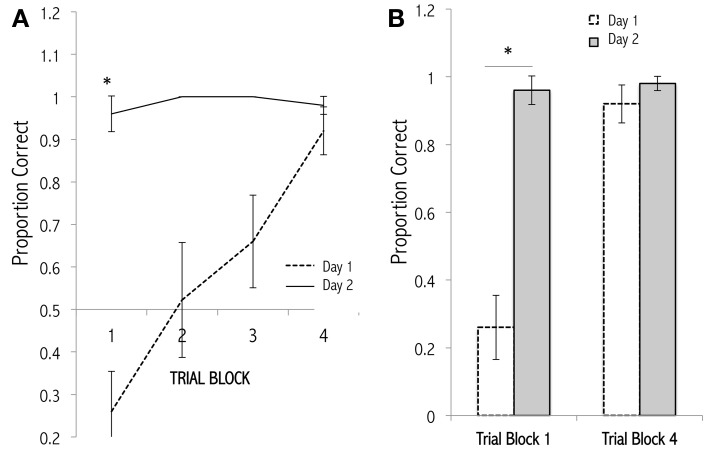
Figure 5.
Learning curves for an odor discrimination task. (A) Mice received 20 trials of discrimination training (Cleland et al., 2002) in which they learned to choose a rewarded conditioned odor (1.0 Pa) over a distractor odor (Day 1). Twenty-four hours later, the discrimination training was repeated (Day 2). The correct trials were scored and averaged across animals. Trials are grouped into 4 blocks of 5 consecutive trials for display and analysis. A steady improvement across trials on Day 1 is remembered 1 day later. (B) Data from trial blocks 1 and 4 replotted for comparison. Comparing trial block 1 (trials 1–5) between days, mice performed significantly better on the second training session, indicating a robust retention of odor memory [asterisk: t(8) = 7.5593, p < 0.001]; no other comparisons approach statistical significance. Comparable findings have been observed by Schellinck et al. (2001).