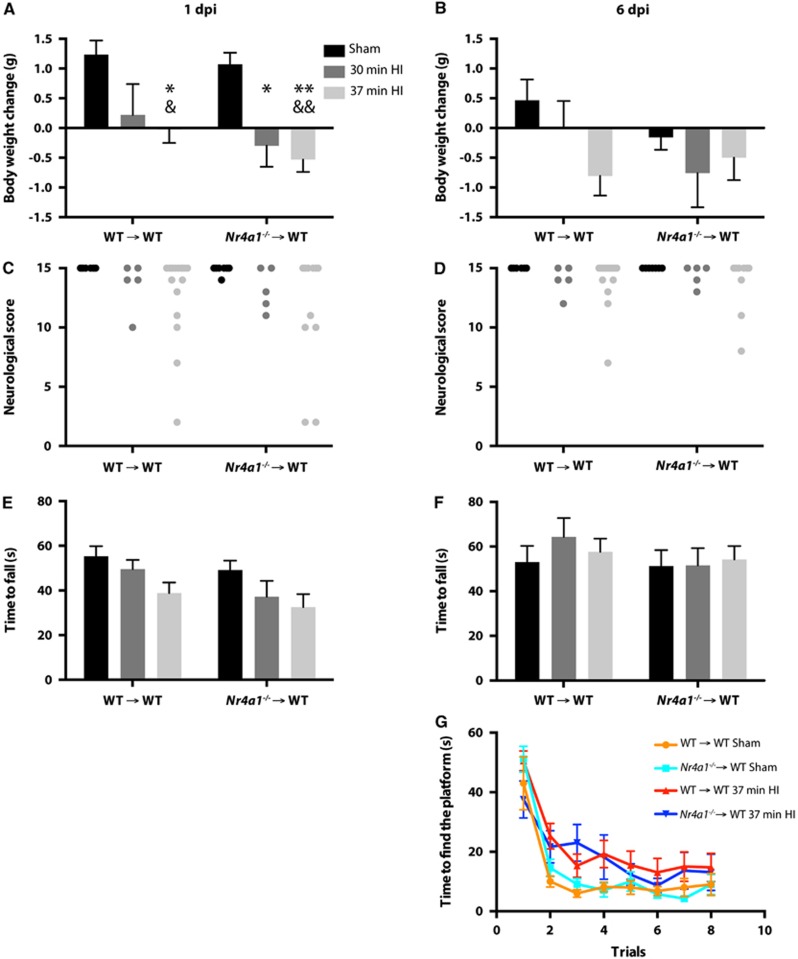
Figure 3.
Physiologic and behavioral outcomes after HI in chimeric mice with Nr4a1−/− or WT hematopoietic system. Nr4a1−/− → WT and WT → WT mice had a sham surgery or were subjected to HI (right common carotid occlusion followed by 30 or 37 minutes of hypoxia). Changes in body weights were measured (A) 1 day or (B) 6 days after the surgery. To assess motor impairments post surgery, mice were evaluated with a neurologic test at (C) day 1 and (D) day 6, and a rotarod test at (E) day 1 and (F) day 6. (G) Hippocampal-dependent spatial learning was evaluated by the latency to find the localization of the platform in the water T-maze test 6 days after the surgery. Significant effects of the HI injuries were detected for A, C, E, and G (trials 2 and 3 only). (Results are expressed as means±s.e.m.; each point represents a single mouse in C and D; n=all the mice alive in Table 1; for two-way analysis of variance (A, B, E, F, G), the Tukey post hoc test was performed; Kruskal–Wallis test was used in C and D; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 (versus WT → WT sham); &P<0.05, &&P<0.01 (versus Nr4a1−/− → WT sham)). HI, hypoxia-ischemia; WT, wild type.