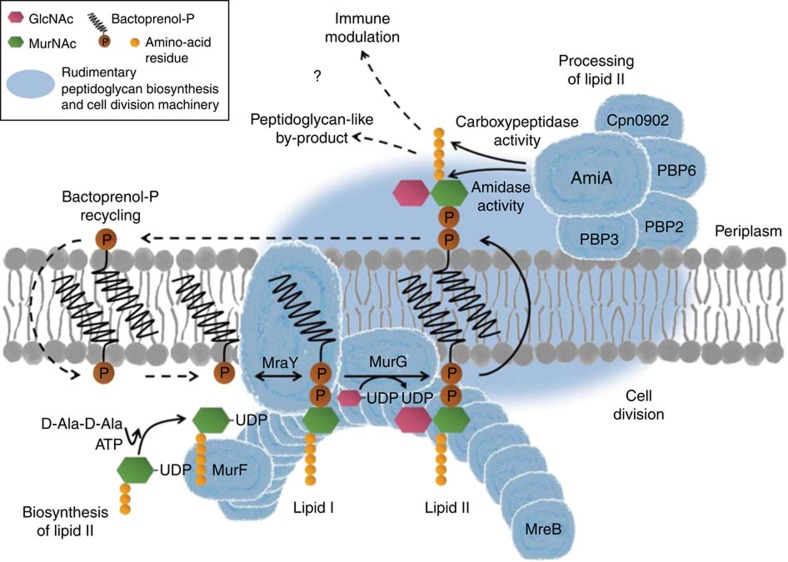
Figure 6. Proposed model for the role of the conserved lipid II pathway in maintaining a functional cell division machinery and contributing to modulation of host response in Chlamydiaceae.
A complete cycle of lipid II biosynthesis, processing and recycling needs to be maintained for coordinated function of the cell division machinery. Structural protein MreB (in interaction with RodZ) functionally organizes MurF, MraY and MurG, three key components in lipid II biosynthesis, at the septum. The synthesized precursor is translocated to the outside and processed by a rudimentary cell wall biosynthesis/cell division machinery. DD-CPase activity of AmiA, together with PBP6 and Cpn0902 (NlpD), might orchestrate DD-CPase functions in chlamydial cell division. Amidase activity of AmiA would play a central role in processing lipid II by releasing the pentapeptide side chain to allow for (i) transpeptidation of pentapeptides catalysed by monofunctional transpeptidases FtsI and PBP2 and for (ii) regulation of host immune response due to blocking of Nod2 sensing. FtsZ as well as transglycosylases, endopeptidases and pyrophosphorylases are not found in Chlamydiaceae. Dashed arrows and question marks indicate steps of the proposed pathway that remain to be elucidated. (GlcNAc: N-acetylglucosamine; MurNAc: N-acetylmuramic acid).