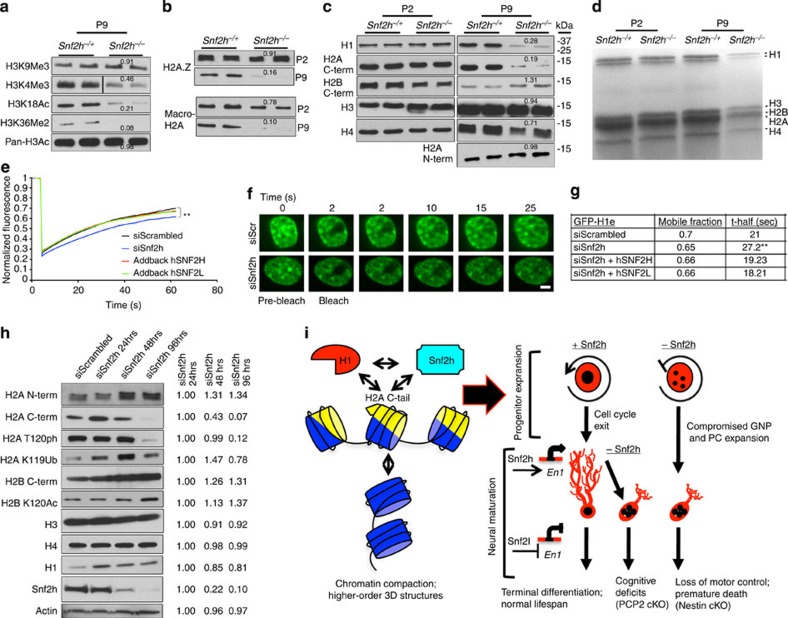
Figure 9. Snf2h mediates chromatin transitions through linker histone H1 dynamics.
(a,b) Immunoblots of acid-extracted cerebellar histones from Snf2h cKO-Nes (Snf2h−/−) and control littermates (Snf2h−/+) for (a) histone H3 post-translational modifications at P9; or (b) histone variants H2A.Z and macro-H2A at P2 and P9. Values denote average densitometry relative to control samples (n=4). (c) Immunoblots of core histones from P2 and P9 cerebellar extracts from Snf2h cKO-Nes and control littermates. Values denote average densitometry relative to control samples (n=4). (d) Colloidal blue staining of isolated P2 and P9 histones from Snf2h cKO-Nes and control littermates to examine stoichiometry. (e) Mean normalized GFP-H1e FRAP curves of siScrambled (siScr); siSnf2h; siSnf2h+addback human (h) SNF2H; or siSnf2h+addback hSNF2L from transiently transfected mouse Neuro2A cells 48 h after treatment. A significant difference between recovery curves of siScrambled and siSnf2h is indicated. **P=0.008, n=20, Student’s t-test. Error bars were omitted for clarity. (f) FRAP images of GFP-H1e from siScr (top) or siSnf2h (bottom) Neuro2A treated cells at the indicated times. Scale bar, 1 μm. (g) Mobile fractions and t-half values for GFP-H1e FRAP experiments. **P=0.008, n=20, Student’s t-test. (h) Histone immunoblots of Neuro2A cells treated with siScr or siSnf2h for the indicated times. Snf2h KD is observed by 48 h. Actin served as loading control. Values denote average densitometry relative to siSnf2h 24 h treatment. (n=4). (i) Proposed model of Snf2h-dependent chromatin organization. Left, Snf2h interacts with the C-terminal tail of H2A to mediate histone H1 deposition and promote higher-order chromatin compaction and terminal differentiation32. Right-top, Snf2h is required for normal progression through the cell cycle35,37. Snf2h cKO-Nes mice have compromised expansion of the GNP and PC progenitor pools resulting in cerebellar atrophy. Right-bottom, after cell cycle exit, Snf2h- and Snf2l-dependent chromatin remodelling drives the establishment and maintenance of gene expression profiles. The co-regulation at the En1 locus is depicted as an example and this regulation promotes neural maturation. The embryonic removal of Snf2h (Nestin model) results in cerebellar hypoplasia and reduced dendritic arborization of PCs, causing severe ataxia and premature death. Similarly, Snf2h ablation in PCs (PCP2 model) also affects PC arborization, but conversely results in cognitive deficits rather than motor alterations.