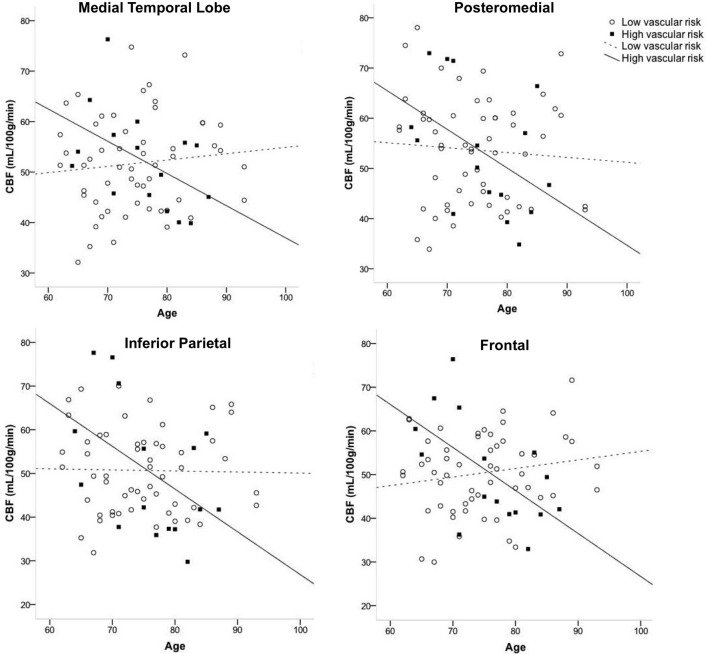
Figure 1.
Interaction of age and vascular risk burden on cerebral blood flow (CBF) for four a priori cortical regions of interest. Interactions were statistically significant for the medial temporal, inferior parietal, and frontal regions of interest (p-values < 0.05) and there was a trend toward an interaction for posteromedial CBF (p = 0.12). High vascular risk indicates the presence of two or more vascular risk factors whereas low vascular risk indicates the presence of no or one vascular risk factor.