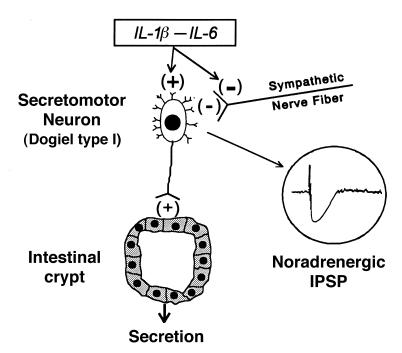
Figure 13.
Conceptual model for actions of IL-1β and IL-6 in the enteric nervous system. Both cytokines act directly to increase excitability of neurons and to suppress release of norepinephrine at sympathetic synapses on submucous neurons. Stimulation of submucosal secretomotor neurons is expected to evoke secretion from mucosal crypts and may account in part for diarrheal symptoms associated with proinflammatory cytokines. Inactivation of sympathetic braking action on secretomotor neurons facilitates secretion and may also contribute to diarrheal symptoms.