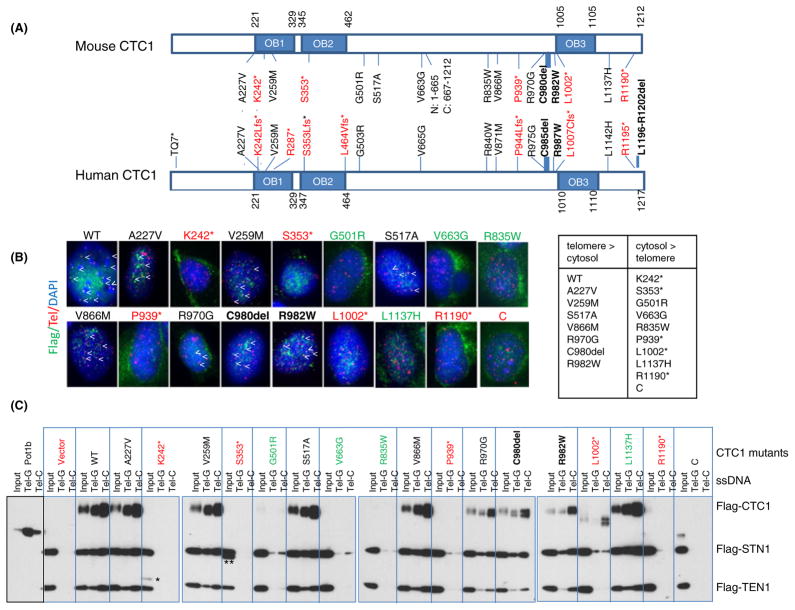
Fig. 1.
CTC1 mutations affect telomere localization. (A) Schematic of all documented human CTC1 mutations. Corresponding mutations in mouse CTC1 analyzed in this study are illustrated. Frameshift mutations (denoted by *) are in red; missense mutations, in black; and in-frame deletions, in black (bold). OB: OB folds. N: N-terminal mutant (aa 1–665); C: C-terminal mutant (aa 667–1212). (B) Telomere PNA-FISH demonstrating the localization of Flag-CTC1WT and several Flag-CTC1 mutants to telomeres in CTC1−/− MEFs. Cells were stained with anti-Flag antibody (green), telomere PNA-FISH with Tam-OO-(CCCTAA)4 telomere peptide nucleic acid (red) and 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI, blue). A minimum of 500 nuclei were analyzed per genotype. Localization of CTC1 to telomeres is indicated by arrowheads. Frameshift mutants are illustrated in red, missense or in-frame mutants that localize to telomeres are in black, and missense mutants that cannot localize to telomeres are in green. C: C-terminal truncation mutant. (C) Impact of CTC1 mutations on CST complex formation on ss telomeric DNA. WT or mutant Flag-CTC1, Flag-STN1, and Flag-TEN1 were co-expressed in 293T cells, purified, and incubated with streptavidin beads bound by biotinylated ss Tel-G (TTAGGG)6 or Tel-C (CCCTAA)6 oligonucleotides. After washing, the DNA bound CST complexes were eluted and detected by immunoblotting. Labeling scheme of mutant CTC1 is the same as in (B). Purified POT1b was used as a positive control for preferential binding to Tel-G oligos. C: C-terminal truncation mutant; *: K242*; **: CTC1S353* truncated protein products.