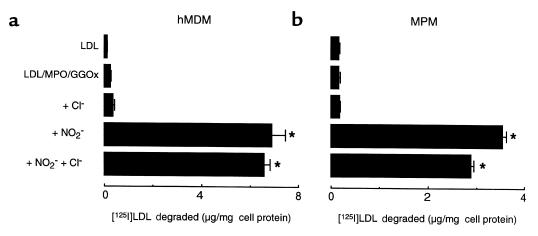
Figure 2.
Degradation of [125I]LDL by hMDMs and MPMs after modification by MPO-generated chlorinating and nitrating intermediates. [125I]LDL (0.2 mg/mL) was incubated with isolated human MPO (30 nM), glucose (100 μM), and glucose oxidase (20 ng/mL) in the presence of the indicated additions in sodium phosphate buffer (50 mM, pH 7.0) supplemented with DTPA (100 μM) overnight at 37°C, as described in Methods. Under these conditions, a constant flux of H2O2 (0.18 μM/min) is generated by the GGOx system. Reactions were stopped by addition of BHT (40 μM) and catalase (300 nM), and then 125I-labeled lipoproteins (5 μg/mL) were incubated with either hMDMs (a) or thioglycollate-elicited MPMs (b) at 37°C for 5 hours in the appropriate media containing additional catalase (300 nM) and BHT (20 μM). Cellular uptake of lipoproteins was subsequently determined as described in Methods. When indicated, Cl– (100 mM) or NO2– (500 μM) were added during LDL modification by MPO. Data represent the mean ± SD of triplicate determinations. Similar results were observed in 3 independent experiments. *P < 0.001 for comparison vs. LDL modified in the presence of MPO and an H2O2-generating system (LDL/MPO/GGOx).