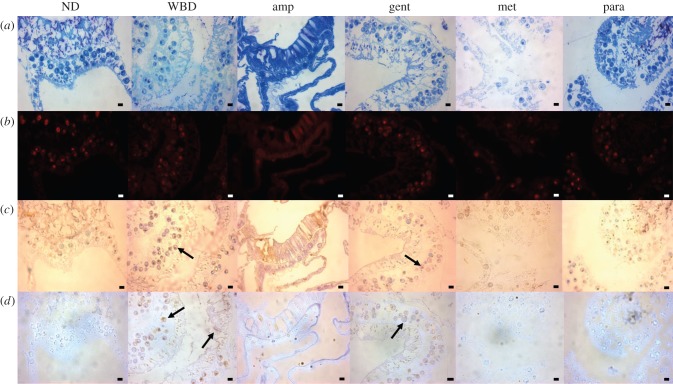
Figure 4.
Representative histological sections from each treatment at day 6 of the experiment for non-diseased tissues (ND) and those treated with paromomycin sulfate (para), ampicilin (amp) and gentamicin (gent). The white band diseased (WBD) tissues and those treated with metronidazole (met) were sampled before complete tissue loss occurred, on days 2, 3, 4 and 5 (table 1). In all cases (except that of ND tissues), the samples were taken at the disease lesion interface, within 1 mm of the lesion boundary. (a) Sections stained with Toluidine blue. Tissues appear indistinguishable from healthy samples in the diseased (WBD) samples and in all treatments except for the Met treatment, in which extensive tissue fragmentation can be seen. (b) Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) probed with EUBMIX, giving a comprehensive ‘eubacterial’ detection as visualized by red (CY3) fluorescence. In this case, few if any bacterial-sized fluorescent particles can be identified in the sections, with red fluorescence attributed to autofluorescence of symbiotic algae and nematocysts. (c) In situ end labelling (ISEL), programmed cell death assay. Little or no probe binding (indicated by red-brown staining) could be detected in ND tissues and those treated with amp and para. Positive ISEL staining was observed in diseased tissues (WBD) and gent-treated samples (arrows). (d) Nigrosin (Nig) staining, which targets necrotic tissues. Brown-stained (necrotic) host tissues and symbiotic algae were observed in diseased (WBD) and gent treatments (arrows), but not in any other samples. Para- and amp-treated tissues appeared indistinguishable from healthy tissue sections in all cases. Scale bars represent 10 µm. (Online version in colour.)