Figure 1.
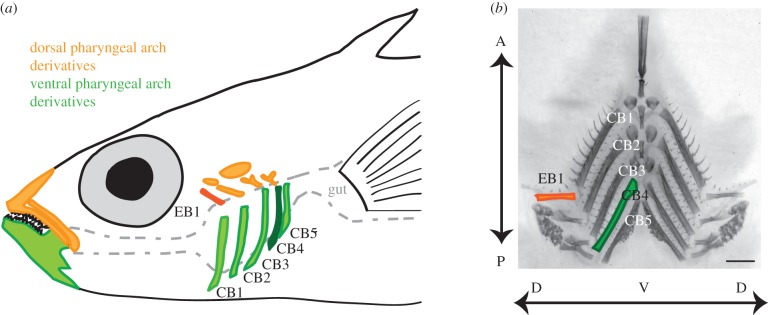
Anatomy of stickleback branchial bones. (a) Fish ingest food into the buccal cavity, which is flanked bilaterally by dorsal (epibranchial, EB; orange) and ventral (ceratobranchial, CB; green) pharyngeal arch bones between the mouth and the gut. Also shown are the upper and lower oral jaw, segmental homologues of the branchial bones in the first pharyngeal arch. In some experiments, we focused on the highlighted bones: EB1 and CB4, the dorsal and ventral bones with the strongest detected genetic effects. Some bones have been omitted for clarity. (b) Dissected and flat-mounted Alizarin red-stained branchial skeleton with dorsal (EB1) and ventral (CB1–CB5) bones indicated. Dorsal–ventral (DV) and anterior–posterior (AP) axes are labelled with arrows. Scale bar, 1 mm.
