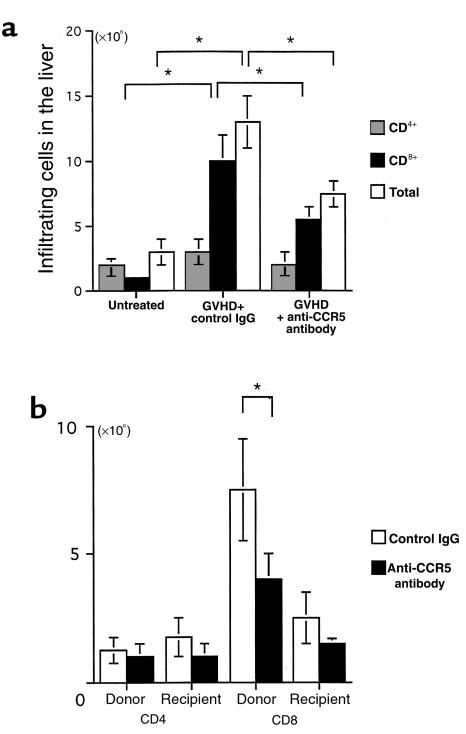
Figure 2.
Effect of anti-CCR5 antibody on intrahepatic infiltration of mononuclear cells. (a) The number of CD4+ (dotted bars) and CD8+ (filled bars) T cells was determined by multiplying the total leukocyte number (open bars) by the fractions representing the CD4+ and CD8+ populations. Liver-infiltrating leukocytes were prepared from untreated mice and GVHD-induced mice treated with either control antibody or anti-CCR5 antibody. (b) Effect of anti-CCR5 antibody on the chimerism at the second week after induction. The number of donor-derived cells and recipient-derived cells was determined by multiplying the total leukocyte number by the fractions representing the H-2Dd–negative and H-2Dd–positive populations, respectively. Moreover, by multiplying the donor cell number and the recipient cell number by the fraction of CD4+ and CD8+ cells, the chimerism was determined in the GVHD-induced mice. Open bars: control antibody; filled bars: anti-CCR5 antibody. The mean ± SD of 6 mice is shown here. Five independent experiments were performed. *P < 0.05.