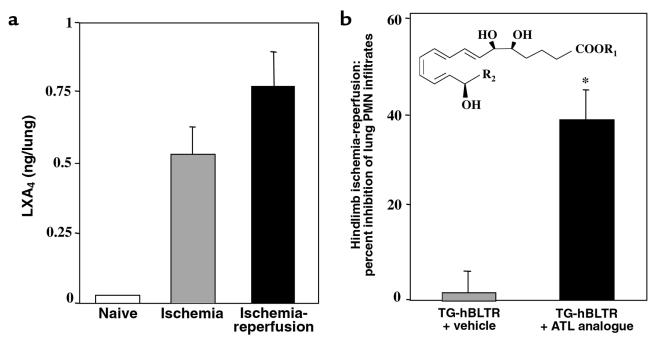
Figure 6.
ATL inhibits PMN infiltration into lungs after hindlimb ischemia-reperfusion. (a) BALB/c mice were subjected to ischemia-reperfusion (∼0.8 ng; filled bar) or ischemia alone (∼0.5 ng; hatched bar). After removal of hindlimb tourniquet, left lungs were collected with or without reperfusion. LXA4 present within each lung tissue was quantitated by ELISA (Neogen Corp., Lexington, Kentucky, USA) or LC/MS/MS. (b) hBLTR TG mice were injected with vehicle (hatched bar) or the ATL analogue (10 μg; filled bar) [inset: ATL analogue template R2 = (para-fluoro)-phenoxy]. Leukocyte MPO values were obtained from left lung of each mouse after ischemia-reperfusion and were expressed as percent inhibition of lung PMN infiltration. Values from mice that received ATL analogue (∼7 × 105 PMN) versus vehicle alone (∼12 × 105 PMN) were significantly different (*P = 0.04; n = 3).