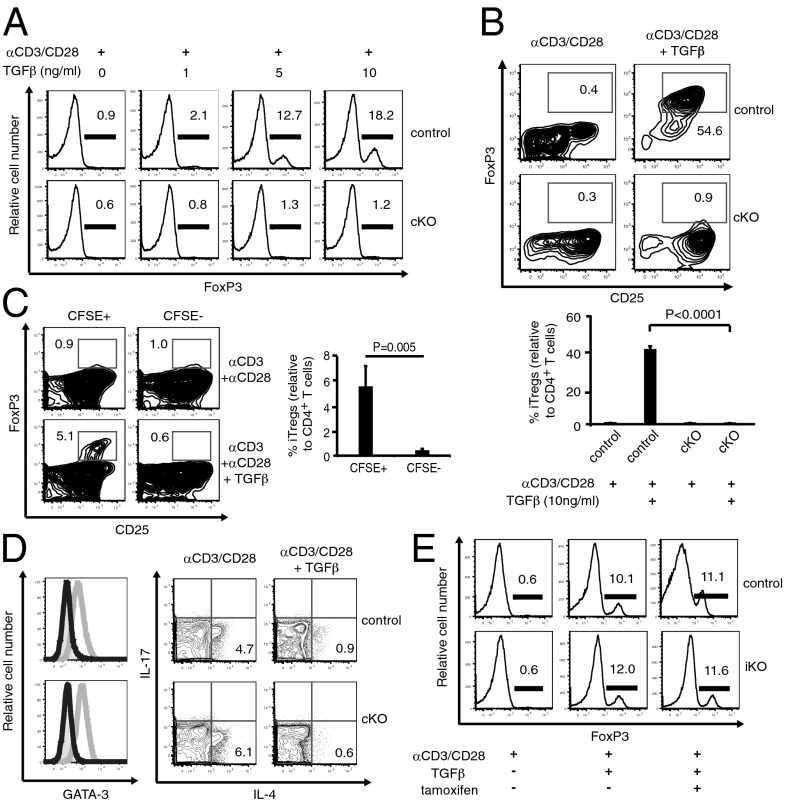
Fig. 2.
KLF2 is required for the ex vivo generation of iTregs. (A) Ex vivo generation of iTregs from splenic CD4+CD25− T cells derived from Klf2fl/fl (control) or Lck-cre; Klf2fl/fl (cKO) mice. Histograms display FoxP3+ T-cell frequencies. This experiment was repeated four times. (B) iTreg development using CD4+CD8−CD25− thymocytes from Klf2fl/fl (control) vs. Lck-cre; Klf2fl/fl (cKO) mice. Representative contour plots (Upper) and a chart of accumulated data (Lower) from four mice per cohort are shown. This experiment was repeated three times. (C) Ex vivo generation of iTregs using cocultured CD4+CD25− T cells harvested from Klf2fl/fl (CFSE+) and Lck-cre; Klf2fl/fl (CFSE−) mice. Contour plots and pooled results for Treg induction (αCD3+αCD28+TGFβ) are shown. This experiment was repeated three times. (D) CD4+ T cells from Klf2fl/fl (control) vs. Lck-cre; Klf2fl/fl (cKO) mice were evaluated for their propensity to skew toward the TH2 lineage and secrete IL-4. (Left) Histogram overlays of GATA-3 expression after culturing conditions that favor CD4+ T-cell differentiation toward a neutral (solid gray), TH2 (gray line), or iTreg lineage (black line). (Right) Generation of intracellular cytokines after CD4+ T-cell activation (Left) vs. iTreg differentiation (Right). This experiment was performed twice. (E) Tamoxifen-induced excision of Klf2 after ex vivo generation of iTregs using CD4+CD25− T cells from T2cre vs. T2cre; Klf2fl/fl animals. T cells from T2cre; Klf2fl/fl mice excised >95% Klf2 as measured by RT-PCR. This experiment was repeated twice.