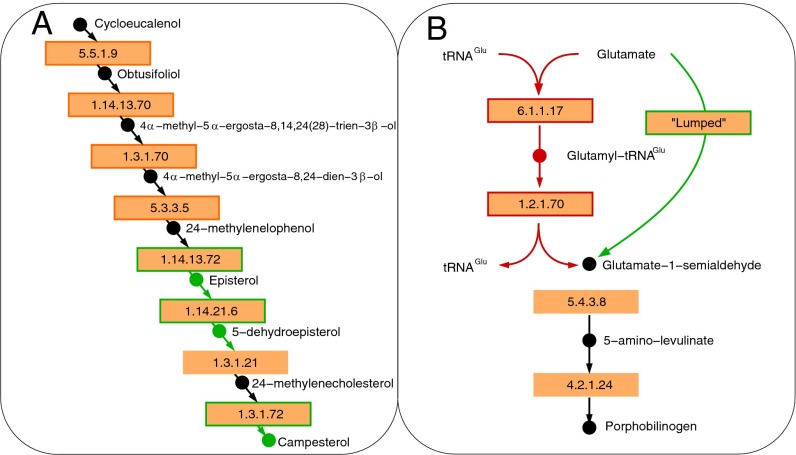
Fig. 3.
Examples of essential and pathway gapfilling results performed on the A. thaliana metabolic reconstruction generated by PlantSEED. (A) Essential gapfilling identified and filled the necessary reactions for the biosynthesis pathway of campesterol (all reactions shown are gap-filling reactions). This sterol is a biomass component, but its biosynthesis is not yet covered in PlantSEED subsystems. The missing reactions were added from the “Plant sterol biosynthesis” pathway in AraCyc (PWY-2541; boxes outlined in red) and the “Steroid biosynthesis” pathway in KEGG (map00100; boxes outlined in green). (B) Pathway gapfilling identified and filled a gap in the biosynthesis pathway of porphobilinogen. The tRNAGlu and glutamyl-tRNAGlu compounds in the original AraCyc representation of this pathway (boxes outlined in red) were excluded from the model because of their lack of molecular formulas, leaving the porphobilinogen pathway incomplete. The process focused on activating reaction–gene associations further downstream, such as AT1G50170 annotated as “uroporphyrinogen-III methyltransferase (EC 2.1.1.107)” (47) and identified an alternative version of this pathway in which the undefined intermediates were lumped out (box outlined in green), completing the pathway and enabling biosynthesis of many heme-like compounds.