Fig. 4.
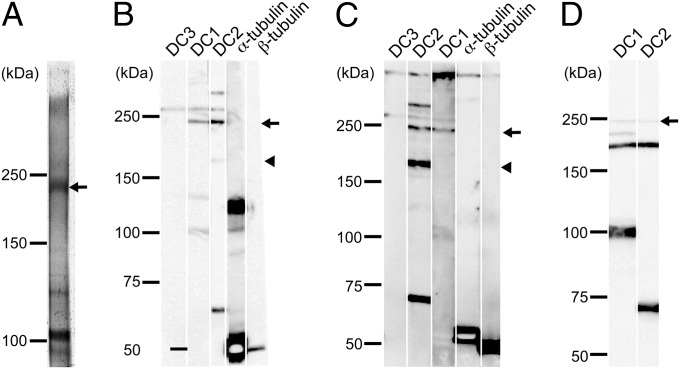
ODA-DCs associate with each other in situ. (A) Silver-stained gel of anti-DC1 immunoprecipitate of products from cross-linked oda6 axonemes. Isolated axonemes of oda6 were cross-linked with BMH, solubilized with SDS, and the solute subjected to immunoprecipitation using the anti-DC1 antibody. Because mass spectrometry revealed that the ∼230-kDa product contained only DC1 and DC2 peptides (Fig. S2), the product is likely to be composed of one DC1 and two DC2s. (B) oda6 axonemes or (C) cytoplasmic microtubules mixed with DC1–2–3 were chemically cross-linked with BMH and the products were analyzed by Western blotting using anti-DC1, -DC2, -DC3, –α-tubulin, and –β-tubulin antibodies. An ∼230-kDa product (arrow) was detected by anti-DC1 and -DC2 antibodies in both samples. Note that an ∼260-kDa product (presumably consisting of one DC1, two DC2s and one DC3) was also detected in both samples. (D) The DC1–2 complex in solution was chemically cross-linked with 1 μM BMH and the results analyzed in a Western blot probed with anti-DC1 and -DC2 antibodies. Two products (∼240 kDa and ∼190 kDa) were detected by both antibodies. Based on the apparent molecular weights of DC1 and DC2, it seems likely that the former is composed of one DC1 and two DC2s, and the latter is composed of one DC1 and one DC2.