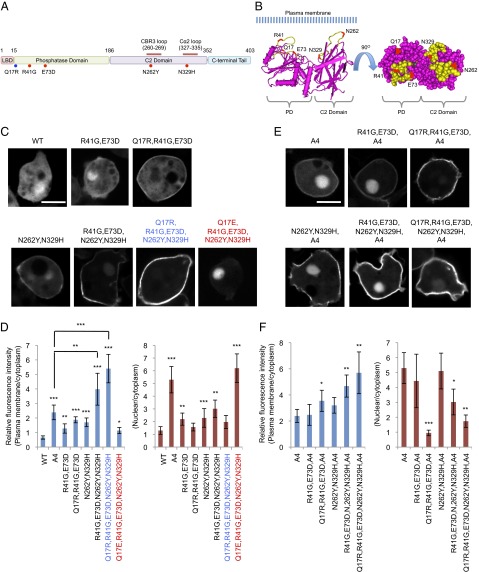
Fig. 4.
ePTEN-GFP (PTENQ17R, R41G, E73D, N262Y, N329H-GFP) is highly enriched at the plasma membrane. (A) The domain structure of PTEN and the position of mutations are shown. Mutations that affect membrane binding and tail interaction are colored in blue and red, respectively. (B) The 3D structure of PTEN suggests that Q17, R41, E37, N329, and N262Y form an interface that binds to the plasma membrane at the surface of PTEN (34) (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/mmdb/mmdbsrv.cgi?uid=11638). (C–F) Dictyostelium cells expressing different forms of PTEN-GFP (C) and PTENA4-GFP (E) were observed by fluorescence microscopy. (Scale bar, 10 µm.) (D and F) Intensity of GFP at the plasma membrane was quantified relative to that in the cytosol. Values represent the mean ± SD (n ≥ 15).