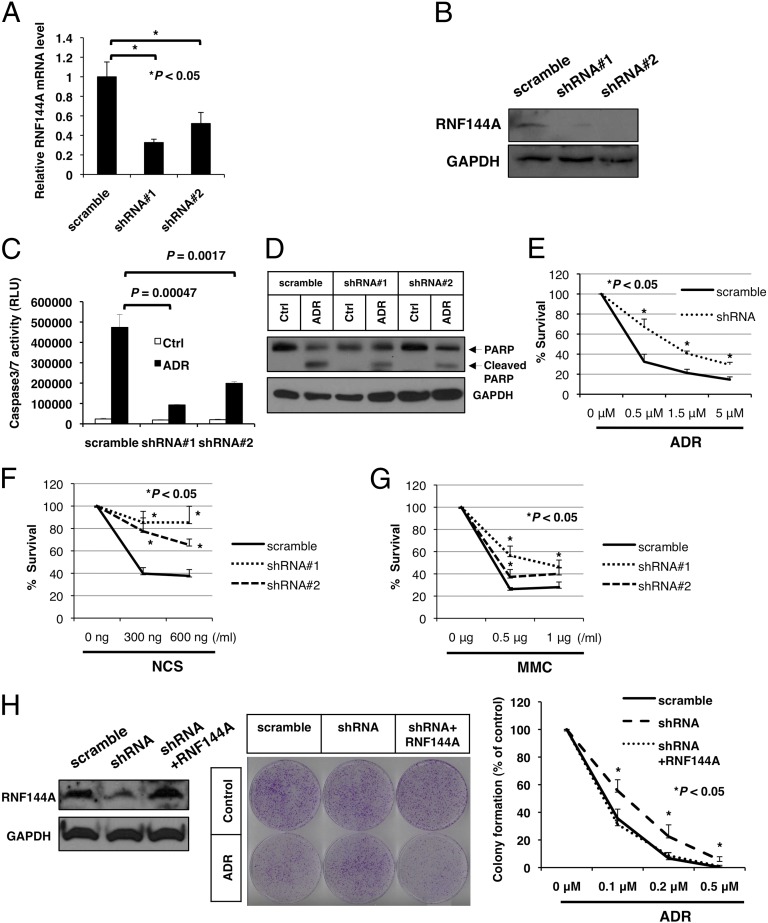
Fig. 2.
RNF144A promotes apoptosis during DNA damage. (A and B) U2OS cells were transfected with two different RNF144A shRNA constructs containing a puromycin-resistant gene and then selected by puromycin for 3 wk. Stable cells were used in the subsequent experiments. (A) Real-time quantitative PCR and (B) Western blot were performed to confirm the establishment of RNF144A-knockdown U2OS stable cells. (C and D) Knockdown of RNF144A reduced ADR-mediated activation of caspase 3/7 and PARP cleavage. RNF144A-depleted U2OS stable cells were treated with ADR (5 μM) or vehicle control (Ctrl) for (C) 6 or (D) 10 h. (C) Caspase 3/7 activity assay and (D) Western blot analysis for cleavage of PARP were then performed. RLU, relative light units. (E–H) RNF144A promoted cell death during DNA damage response. Stable RNF144A knockdown cells were treated with indicated concentrations of (E) ADR, (F) NCS, and (G) mitomycin C (MMC) for 24 h. (H) RNF144A was transfected into RNF144A-knockdown U2OS cells to rescue its expression. (Left) After 2 wk of G418 selection for stable RNF144A transfection, cell lysates were harvested for immunoblotting to confirm rescue of RNF144A expression. The cells were then either mock-treated (control) or treated with ADR for 3 h and released for 10 d. Cell viability was determined by colony formation assay. (Center) Representative images of experiment after ADR (20 nM) treatment. (Right) Repeated experiments with ADR ranging from 0 to 0.5 μM. All results were derived from three independent experiments. Error bars represent SDs. *Significant difference with P < 0.05 (two-tailed t test).