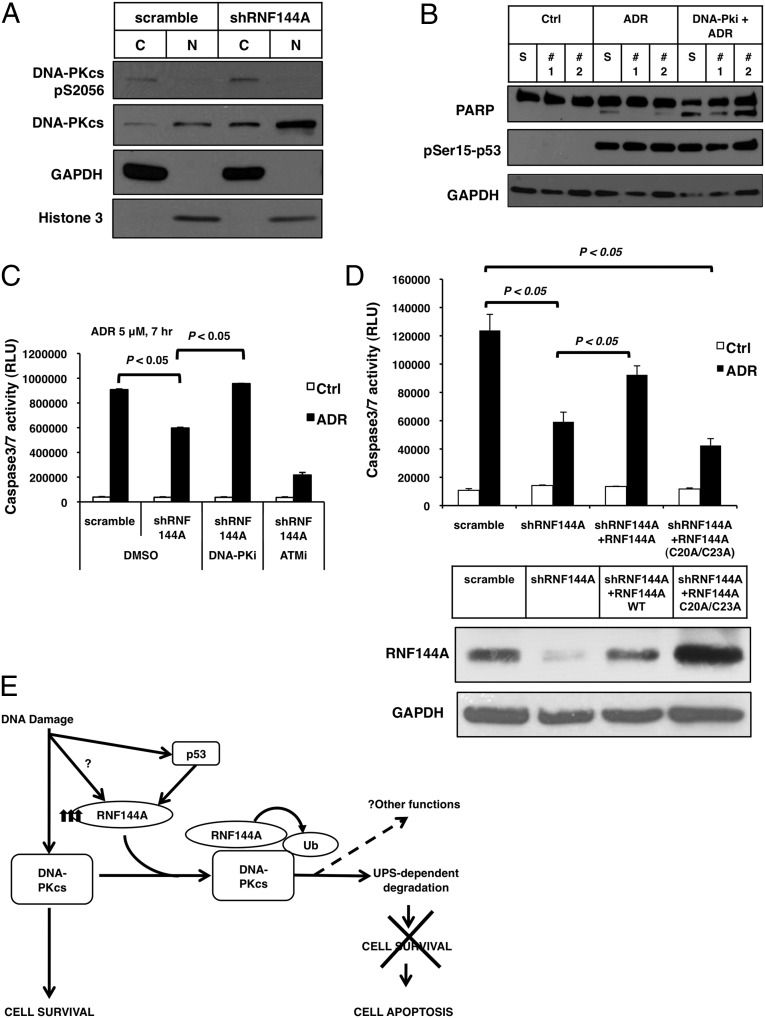
Fig. 6.
RNF144A down-regulates DNA-PKcs to promote apoptosis during DNA damage. (A) Depletion of RNF144A increased pS2056–DNA-PKcs in the cytosol and total DNA-PKcs in both cytosol and nucleus. RNF144A-depleted stable U2OS cells were harvested for subcellular fractionation to separate cytoplasmic (C) and nuclear (N) fractions. Western blot analysis from each fraction was then performed. (B) A DNA-PK inhibitor restored ADR-induced cell apoptosis in RNF144A-depleted cells. S, scrambled shRNA control; #1, RNF144A shRNA#1; #2, shRNA2. RNF144A-depleted stable U2OS cells were treated with ADR (5 μM) for 4 h without or with pretreatment of DNA-PKi before ADR. Cell lysates were then harvested for Western blot analysis as indicated. (C) RNF144A-depleted stable U2OS cells were treated with ADR (5 μM) for 7 h with pretreatment of DNA-PKi or ATMi. Cells were then harvested for caspase 3/7 activity assay. (D) RNF144A (WT and C20A/C23A mutant) were transfected into RNF144A-knockdown U2OS cells to rescue its expression. Cells were treated with ADR (5 μM) for 10 h and then harvested for caspase 3/7 activity assay. (Lower) Because C20A/C23A mutant RNF144A sometimes expressed less than WT (Fig. 4D), to ensure that we had a least equal or more C20A/C23A mutant RNF144A expression than WT, we transfected more C20A/C23A mutant RNF144A plasmid than WT, which accounts for the higher expression of C20A/C23A mutant. (E) A proposed model for how RNF144A down-regulates the prosurvival signaling of DNA-PKcs and promotes cell death during DDR. A basal level of RNF144A may be responsible for other physiological functions or baseline down-regulation of DNA-PKcs. DNA damage stabilizes p53 and induces p53-dependent accumulation of RNF144A. RNF144A protein might also be stabilized by yet-to-be-determined mechanism(s). The accumulated RNF144A then interacts with and degrades more DNA-PKcs through the ubiquitin-proteasome system and inhibits the prosurvival function of DNA-PKcs. Through this mechanism, we propose that accumulation of RNF144A may shift the cell fates from cell survival to apoptosis on persistent or severe DNA damage.