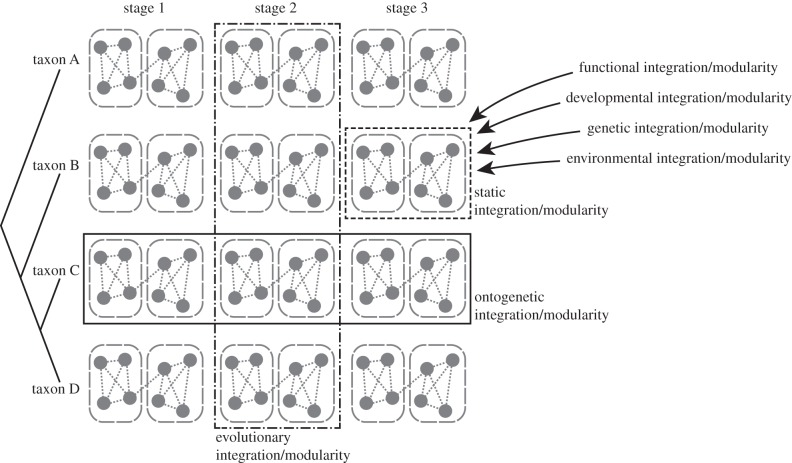
Figure 1.
Different levels of integration and modularity. The diagram contains four related species, each with three ontogenetic stages. Ontogenetic integration and modularity concern the variation across stages within each species, whereas the evolutionary level focuses on the variation among species at any given stage. The static level is within one species and stage. Functional, developmental, genetic and environmental integration and modularity are usually studied in a static context, that is, at one particular ontogenetic stage for a given species. Pooled within-group analyses can be used to summarize patterns.