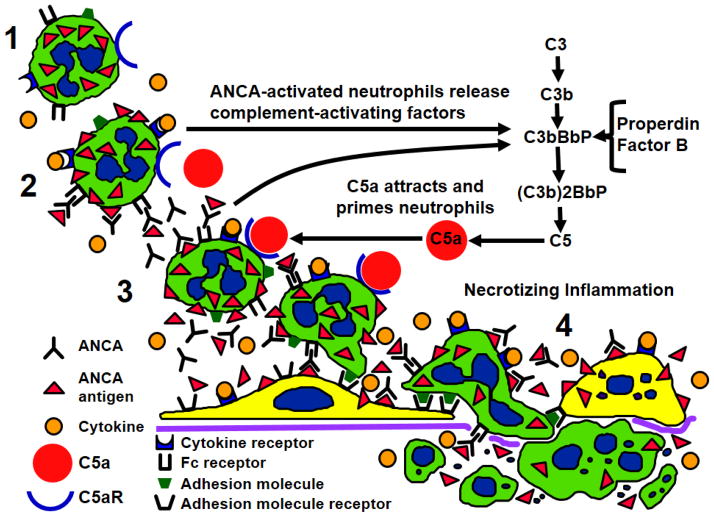
Figure 4.
Depiction of pathogenic events in ANCA vasculitis. 1) Normal unprimed neutrophils have ANCA antigens (e.g. MPO and PR3) sequestered within cytoplasmic granules. 2) Neutrophils that have been primed by cytokines release small amounts of ANCA antigens at the cell surface and in the microenvironment where they are targeted by ANCA. Fc receptor engagement by ANCA bound to ANCA antigens as well as Fab’2 binding to ANCA antigens on the cell surface activates neutrophils. 3) Activated neutrophils release factors that activate the alternative complement pathway with the generation of C5a. C5a is a potent chemoattractant for neutrophils and attracts more neutrophils to the nidus of inflammation, and C5a engages C5a receptor (CD88) resulting in additional priming of neutrophils for activation by ANCA. 4) A potent inflammatory amplification loop is established that drives severe necrotizing inflammation in vessel walls.