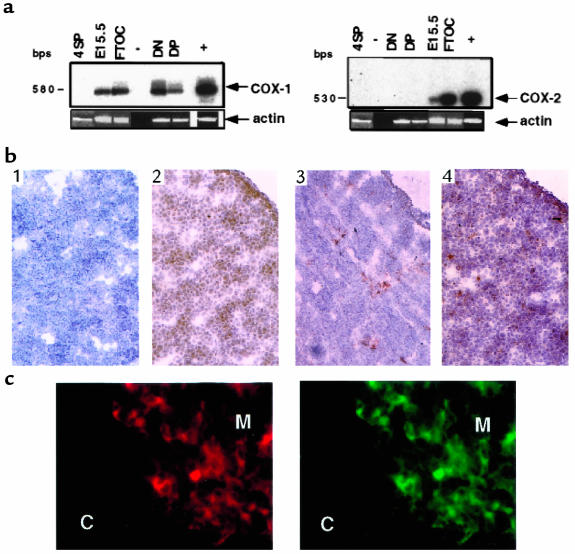
Figure 1.
Characterization of COX-1 and COX-2 mRNA and protein expression. (a) Total RNA from indicated tissues or fractions was isolated, and cDNAs were amplified by RT-PCR using primers specific for COX-1 (left), COX-2 (right), or actin (see Methods). The identity of the amplified fragments for COX-1 or COX-2 was confirmed by Southern blot analysis with specific probes. –, negative control; +, positive control (NIH 3T3 cells); DN, CD4–CD8– thymocytes; DP, CD4+CD8+ thymocytes; 4SP, CD4+ lymphocytes; E15.5, embryonic day 15.5 thymus; FTOC, E15.5 thymus cultured for 5 days. (b) Frozen sections of E15.5 thymus were reacted with normal rabbit IgG as a negative control (panel 1), anti–COX-1 (panel 2), anti–COX-2 (panel 3), and anti–Thy 1.2 (panel 4). Sections were counterstained with hematoxylin. ×40. (c) Frozen sections of thymus from 3-week-old mice were double stained with UEA-1 lectin (left) and anti–COX-2 (right). C, cortex; M, medulla. ×100.