Fig. 1. Phenotypic verification of sarA and saeRS mutants.
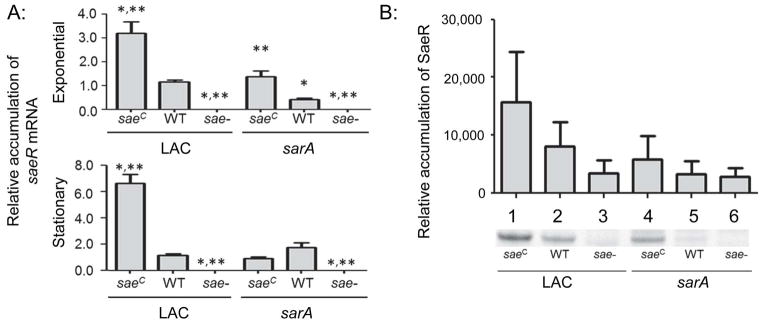
A: The abundance of saeR mRNA was assessed by qRT-PCR in the exponential and stationary growth phases. Strains on the left of each panel as indicated by the underline are strains derived from LAC itself, while strains on the right are derived from the isogenic LAC sarA mutant (e.g. the designation WT on the right indicates results observed with the LAC sarA mutant). Results shown represent the average ± standard deviation from two experiments, each of which was repeated in triplicate. Single asterisk indicates statistical significance by comparison to the LAC parent strain (WT). Double asterisks indicate significance by comparison to the sarA mutant. B: Western blots were performed in triplicate using cell lysates prepared from the same strains and rabbit polyclonal IgG targeting SaeR as primary antibody. Where necessary for legibility, the designation for the constitutively active saeRS derivative (saeRSC) and saeRS mutant were reduced to saeC and sae-respectively.
