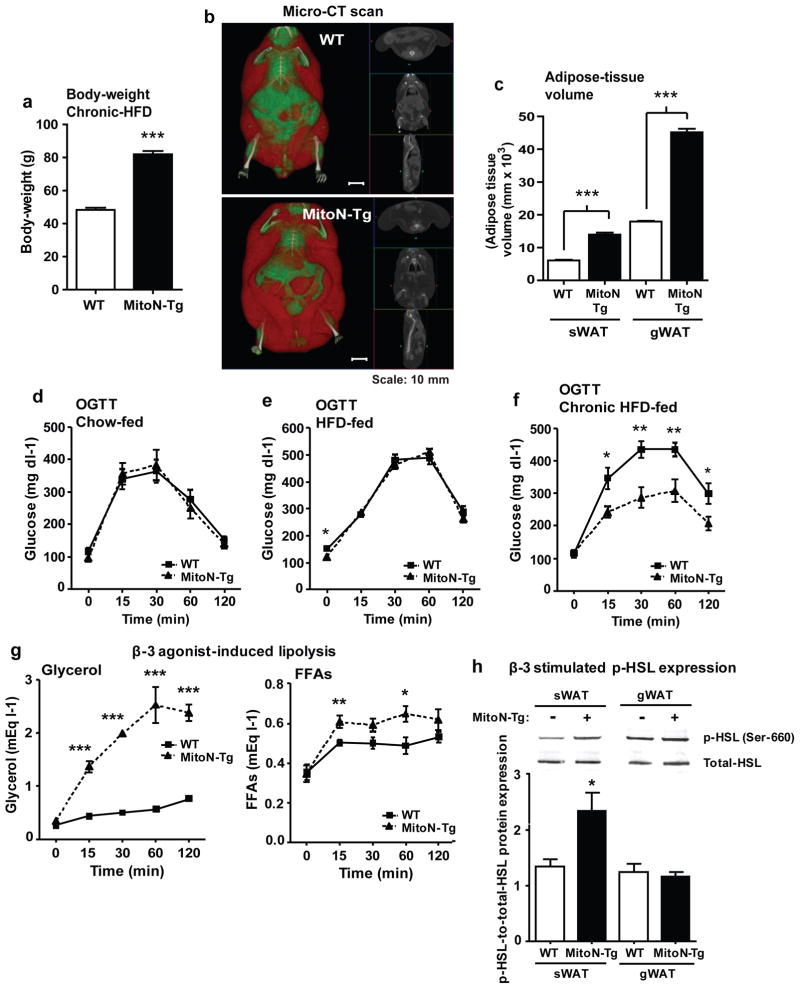
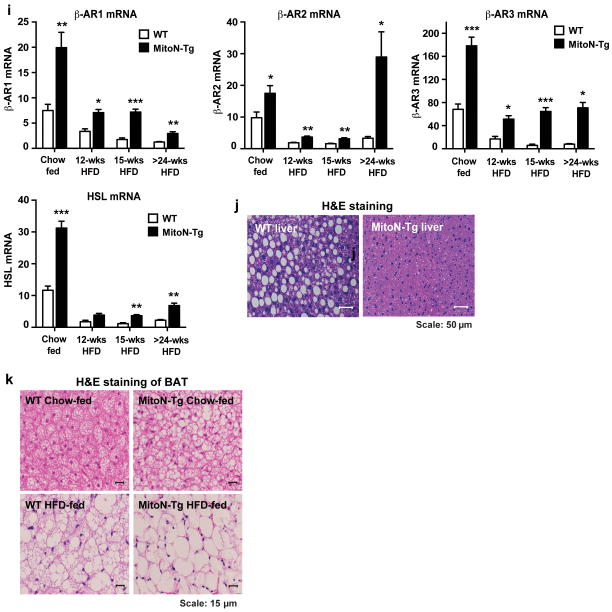
Figure 3. During chronic HFD feeding, MitoN-Tg mice exhibit improved insulin-sensitivity.
(a) Body-weights of WT mice and MitoN-Tg mice following chronic (>15-weeks) HFD feeding (n = 5 per group). (b) A representative whole-body micro-CT scan of a chronic HFD-fed WT mouse (top) and a MitoN-Tg mouse (bottom). Scale bar, 10 mm. (c) sWAT and gWAT volume (mm × 103) (as determined by micro-CT scanning), following >15-weeks of chronic HFD feeding of WT mice and MitoN-Tg mice (n = 5 per group). An oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) (2.5 g kg-1 bodyweight; single gavage) on FVB WT mice and MitoN-Tg mice following (d) chow-diet feeding, (e) 12-weeks of HFD-feeding or, (f) chronic (>15-weeks) HFD feeding (n = 5 per group). (g) Glycerol levels (left) and FFA levels (right) following a β-3 adrenergic agonist sensitivity test (1 mg kg-1 CL316, 243 i.p., single injection; n = 5 per group) of WT mice and MitoN-Tg mice that underwent chronic (>15-weeks) HFD-feeding. (h) Representative immunoblots showing β-3 stimulated (1 mg kg-1 CL316, 243 i.p., single injection) phospho-HSL (p-HSL) (Serine (Ser)-660) (top panel) and total-HSL (bottom panel) protein expression levels in WT and MitoN-Tg sWAT and gWAT fat-pads. Bar graphs show the calculated ratio of p-HSL-to-total-HSL protein expression levels in in WT and MitoN-Tg sWAT and gWAT fat-pads (n = 4 per group). (i) Gene expression levels of β-adrenergic receptor 1 (β-AR1), β-AR2 and β-AR3, in addition to hormone sensitive lipase (HSL) in chow-fed, 12-week HFD-fed, 15-week HFD-fed and chronic (>24-weeks HFD-fed) WT versus MitoN-Tg sWAT. Data represents mean ± s.e.m (n = 5 per group). Student’s t-test, *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001. (j) Representative H&E staining of chronic HFD-fed WT and MitoN-Tg liver tissues. All images were taken at 20X-magnification. Scale bar, 50 μm. (k) Representative H&E staining of BAT derived from WT mice and MitoN-Tg mice that were chow-fed (top panel) or chronic-HFD fed (bottom panel). Scale bar, 15 μm.