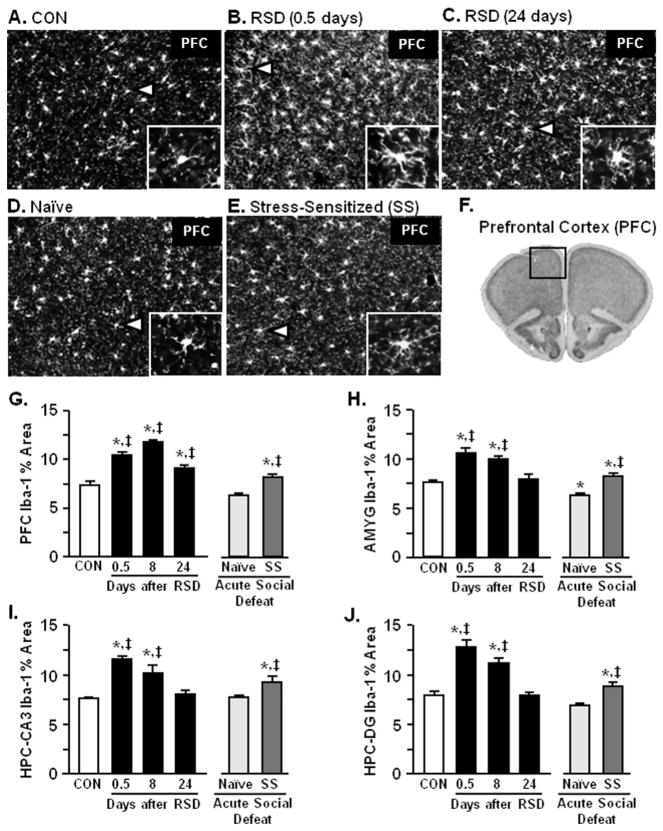
Figure 5.
Microglia in the PFC, amygdala (AMYG), and hippocampus (HPC) exhibited deramified morphology after repeated social defeat (RSD). Brains were collected from control (CON), RSD (0.5, 8, or 24 days later), naïve, and SS mice. Representative images of ionized calcium binding adaptor molecule 1 (Iba-1) labeling in the PFC of (A) CON, (B) RSD (.5 days), (C) RSD (24 days), (D) naïve, and (E) SS mice are shown. (F) Representative section of the area in the PFC used for microglia morphology analyses (64). Repeated social defeat caused microglia activation with increased proportional area of Iba-1 immunofluorescence in the (G) PFC (F5,25 = 22.67, p < .0001), (H) AMYG (F5,25 = 18.26, p < .0001), (I) HPC-cornu ammonis 3 (CA3) (F5,25 = 13.88, p < .0001), and (J) HPC-dentate gyrus (DG) (F5,25 = 18.84, p < .0001) that was reduced over time (except PFC; p < .01). Acute social defeat modestly increased microglia activation in the PFC (p < .01), AMYG (p < .03), HPC-CA3 (p < .02), and HPC-DG (p < .02) of SS mice. Bars represent the mean ± SEM. Means with asterisk (*) are significantly different from CON (p < .05) and means with (‡) are significantly different from naïve (p < .05).