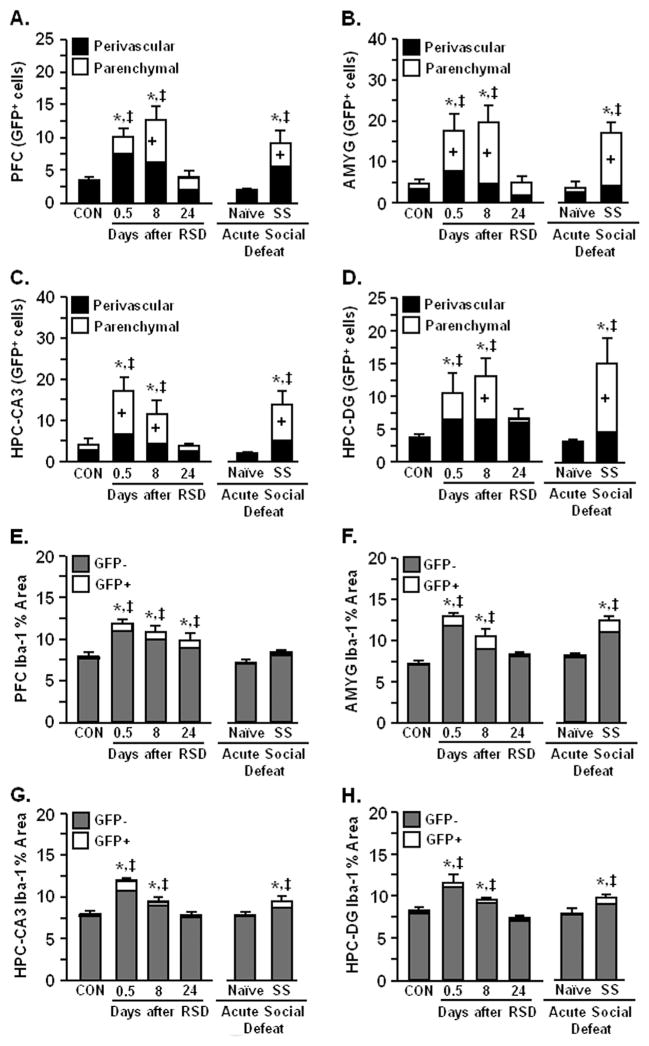
Figure 7.
Acute social defeat in stress-sensitized mice promoted infiltration of bone marrow (BM)-derived macrophages that coincided with microglia activation. Green fluorescent protein (GFP)+ BM-chimera mice were subjected to six cycles of social defeat (repeated social defeat [RSD]) or left undisturbed as control mice (CON). Brains were collected from CON, RSD (0.5, 8, or 24 days later), naïve, and stress-sensitized (SS) mice. The neuroanatomical distribution of GFP+ macrophages was determined and cells were classified as perivascular or parenchymal. Repeated social defeat significantly increased GFP+ perivascular and parenchymal macrophages in (A) prefrontal cortex (PFC) (F5,39 = 8.35, p < .001), (B) amygdala (AMYG) (F5,39 = 7.38, p < .0002), (C) hippocampus (HPC)-cornu ammonis 3 (CA3) (F5,39 = 6.99, p < .0001), and (D) HPC-dentate gyrus (DG) (F5,39 = 4.60, p < .003). At 24 days after RSD, GFP+ macrophages were reduced, but acute social defeat caused robust macrophage infiltration in stress-sensitized mice (p < .05 for each). Repeated social defeat also caused microglia activation with increased ionized calcium binding adaptor molecule 1 (Iba-1) proportional area (GFP+ and GFP−) in the (E) PFC (F5,31 = 9.52, p < .0001), (F) AMYG (F5,26 = 21.10, p < .0001), (G) HPC-CA3 (F5,33 = 16.38, p < .0001), and (H) HPC-DG (F5,33 = 11.35, p < .0001) of BM-chimera mice. Coinciding with macrophage infiltration, RSD-induced microglia activation was diminished 24 days later (except PFC, p < .05). Acute social defeat in stress-sensitized mice also enhanced Iba-1 proportional area in the AMYG, HPC-CA3, and HPC-DG (p < .05 for each). Bars represent the mean + SEM. Means with asterisk (*) are significantly different from CON (p < .05) and means with (‡) are significantly different from naïve (p < .05). Bars with (+) indicate means are significantly different from CON (p < .05).