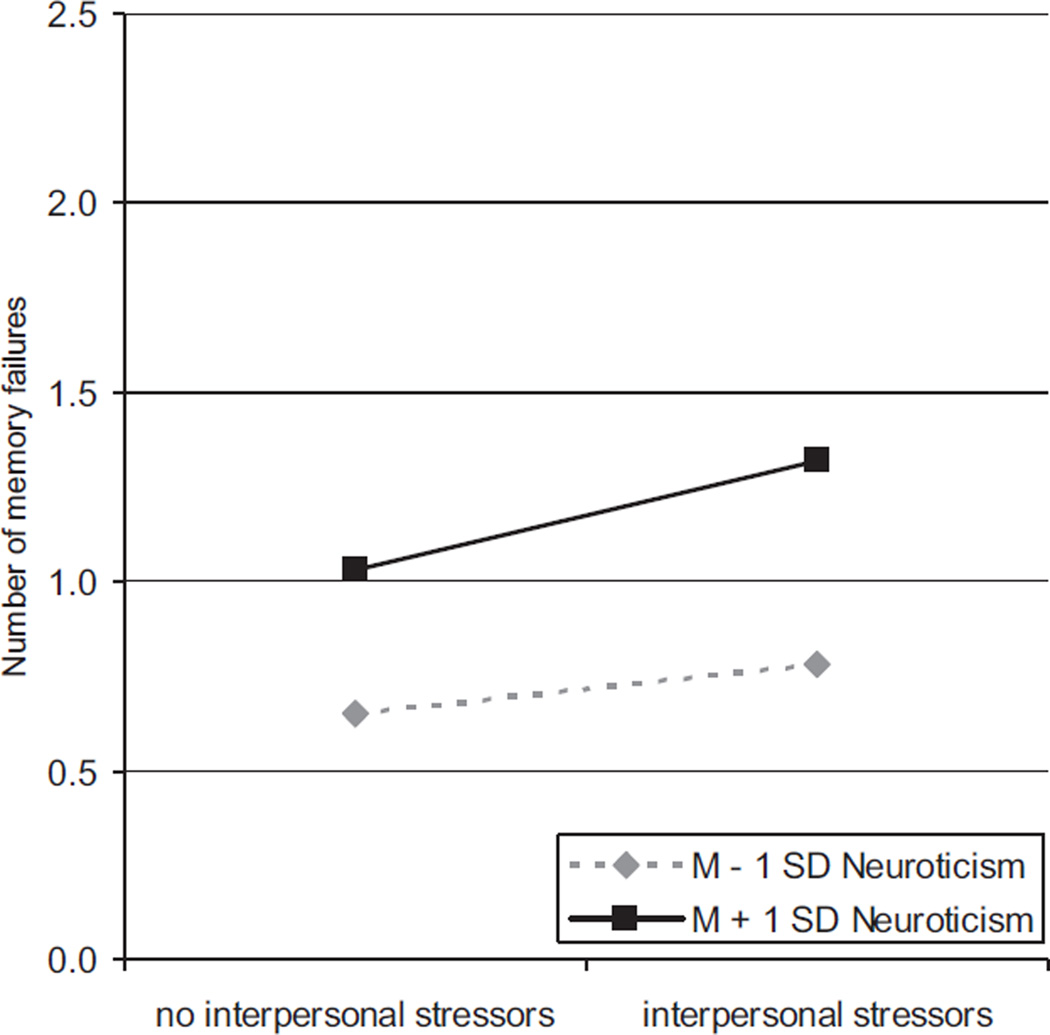
Figure 2.
Predicted values for the cross-level interaction of neuroticism differences in the within-person covariation of interpersonal stressors and memory failures over time. The figure is adjusted for age, gender, self-rated health, and number of life event stressors. People higher in neuroticism (M + 1 SD) were more reactive to interpersonal stressors than those lower in neuroticism (M – 1 SD).