Fig. 2.
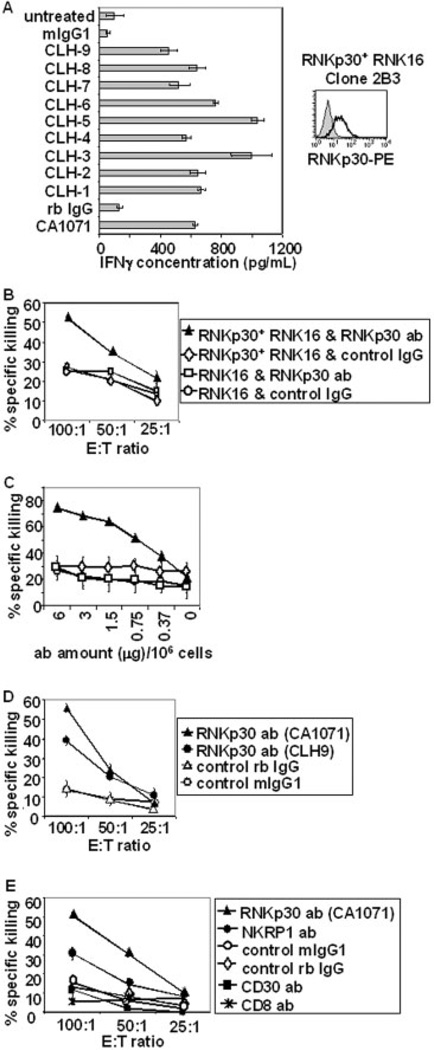
rNKp30 activation in rNKp30+ RNK16 transfectants induces IFN-γ production and cytolytic activity. (A) rNKp30+ RNK16 clone 2B3 cells express rNKp30 as detected by flow cytometry (right). Anti-rNKp30 antibody, CA1071 (open histogram), followed by PE-conjugated secondary antibodies, and not isotype control antibodies (filled histogram), positively stained clone 2B3 cells. On the left, clone 2B3 cells were treated with immobilized antibodies (10 µg/mL) as indicated on the y-axis for 24 h (n=3). Harvested supernatants were analyzed for IFN-γ by ELISA. (B) rNKp30+ RNK16 clone 2B3 and parental RNK16 cells were analyzed for cytolytic activity in 4-h redirected lysis assays against [3H]thymidine-labeled P815 targets (n=8). On the left, rNKp30+ RNK16 cells stimulated with rNKp30 antibody, CA1071 (black triangles), showed increased cytotoxicity with increasing E:T ratios. Target cells were resistant to killing when control IgG or parental RNK16 cells were used (white diamonds, white squares, and white circles). (C) Redirected lysis assays were performed with titrated amounts of rNKp30 antibodies (CA1071) or control antibodies at an E:Tof 100:1 (n=2). Symbols used in (B) and (C) represent the same effector cells and antibody treatments. (D) Redirected lysis assays were performed to compare the anti-rNKp30 antibodies, CA1071 pAb (black triangles) and CLH-9 mAb (black circles). Both anti-rNKp30 antibodies induce killing as compared to control antibodies (white triangles and white circles). A symbol legend for (D) is boxed on the right. (E) Antibodies specific for activation receptors triggered cytotoxicity from rNKp30+ RNK16 cells. Antibodies (2 µg/106 effector cells) against rNKp30 (black triangles), NKRP1A (black circles), CD30 (black squares), CD8 (asterisks), and control mIgG1 (white circles) and control rabbit IgG (white diamonds) were analyzed in redirected killing assays (n=2). A symbol legend for (E) is boxed on the right.