FIGURE 6.
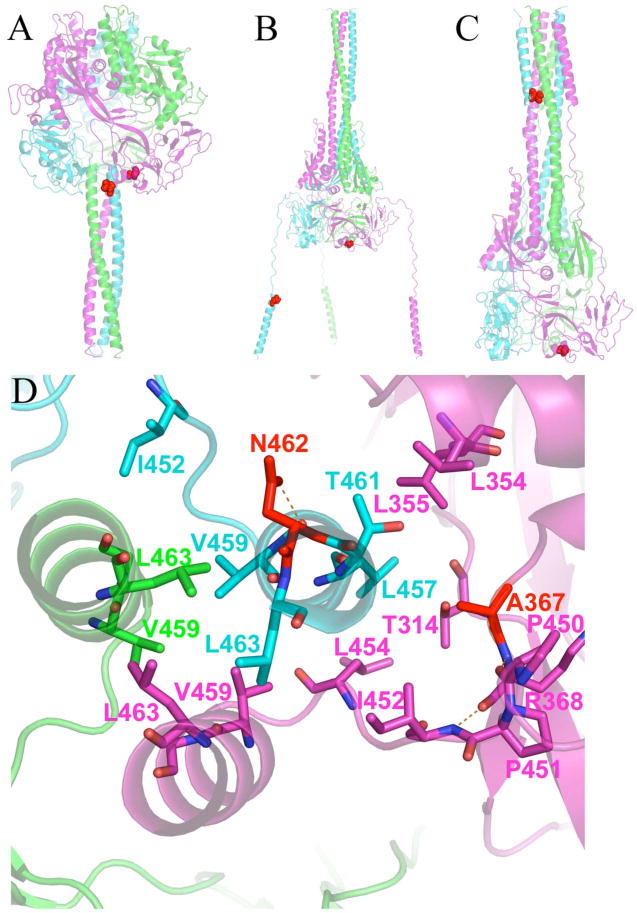
Position of resistance-conferring mutations at Asn462 and Ala367. (A) Pre-fusion model shows that these residues are proximal and part of the key interactions holding HR-B to the head of the protein prior to fusion. (B) Proposed intermediate structure revealing that Asn462 and Ala367 must separate to achieve the conformational intermediate. (C) Post-fusion model showing that Asn462 ends up in the 6HB while Ala367 remains in the DI domain of the MV F head. (D) View of the HR-B/HR-B linker interface with the head of MV F in the pre-fusion model. Residues providing key hydrophobic interactions are shown as sticks. Eight hydrophobic residues provide interaction of the HR-B/HR-B linker to the head. Five of the residues (Leu457, Leu 454, Ile452, Pro451 and Pro450) are from this network. The other three hydrophobic residues (Leu448, Ile446, and Val432, not shown) are located upstream on the HR-B linker.
