Figure 2.
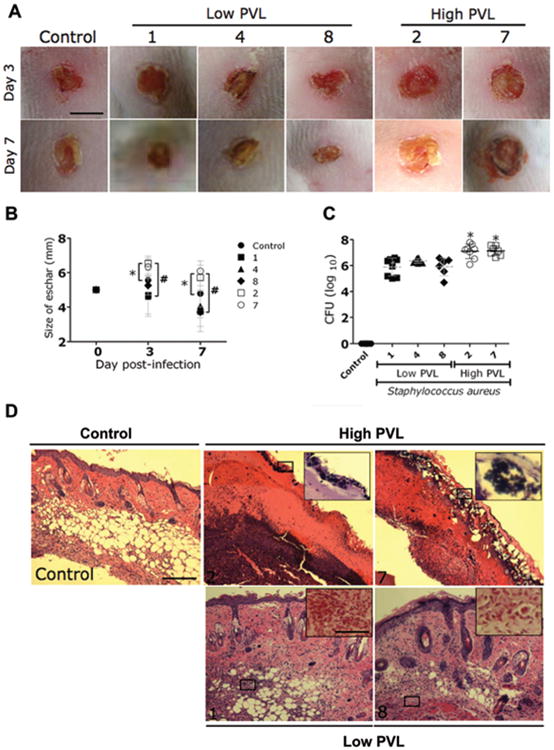
Comparison of virulence of Panton-Valentine leukocidin (PVL)–positive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and methicillin-susceptible S. aureus (MSSA) strains with high and low PVL production in a murine skin and soft-tissue infection (SSTI) model. A, Wounds of BALB/ c mice uninfected (control) or infected with low- or high-PVL-producing strains of S. aureus on days 3 and 7. Scale bar, 5 mm. B, Analysis of wound size in the skin lesions of the mice. Data are the means of the results for 3 measurements at each time point, and error bars denote standard deviations. *P < .05; #P < .001. C, Wound bacterial burden in colony-forming units (CFUs). In mice infected intradermally with 107 CFUs of low-PVL-producing S. aureus strains, the wound bacterial burden was significantly lower than in mice infected with high-PVL-producing S. aureus strains. Uninfected mice were used as a control. There were 8 mice in the control group; 8 mice in each of the groups infected with strains 1, 2, and 4; 7 mice in the group infected with strain 7; and 6 mice in the group infected with strain 8. Dashed lines show the means of the results for 4 measurements, and error bars denote standard deviations. Asterisks denote statistical significance (P < .01), which was calculated by analysis of variance and adjusted by use of the Bonferroni correction. D, Histological analysis of uninfected mice (control) and mice infected with either high- or low-PVL-producing strains on day 7. Shown are representative hematoxylin-eosin–stained sections of the skin lesions, which demonstrate increased inflammation in SSTIs caused by high-PVL-producing S. aureus strains compared with low-PVL-producing strains. The insets show Gram staining of the sections shown in the black rectangles. Few or no S. aureus cells (purple) are seen in the SSTIs caused by low-PVL-producing S. aureus strains. Hematoxylineosin staining scale bar, 25 μm; Gram staining scale bar, 10 μm.
