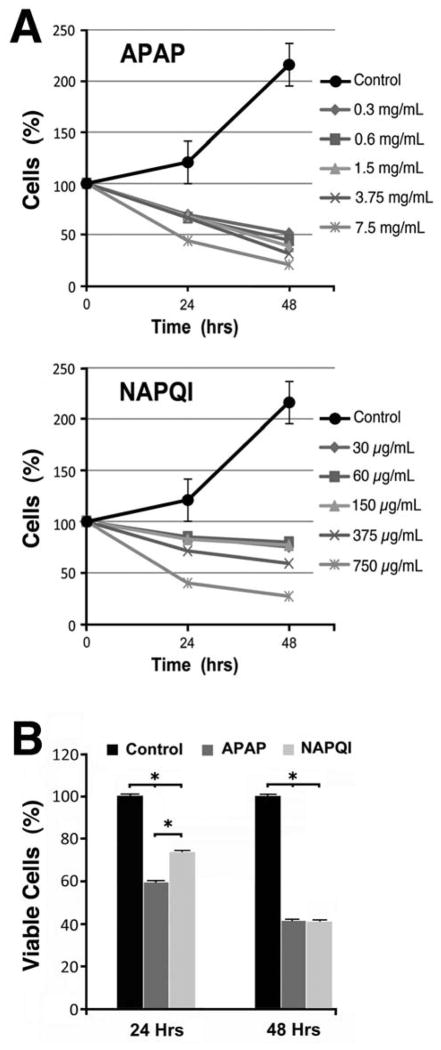
Fig. 1. Effects of APAP and NAPQI on viability of HEI-OC1 cells in culture.
A – Whereas Control cells doubled every 48 hours, direct cell count using an adherent cell cytometer indicated that exposure to APAP or NAPQI significantly decreased their numbers at 24 as well as 48 h. Except for the highest dose, APAP showed more cytotoxicity than NAPQI. B – MTT studies (n=3) confirmed a significant decrease in viability of cells exposed to APAP and NAPQI at both time points. Although APAP effect was stronger than NAPQI’s at 24 h (APAP = 59.4±0.4%, NAPQI = 73.4±0.4%, P≤0.0001*), no differences were evident at 48 h. (APAP = 41.3±0.4%, NAPQI = 41.0±0.4%, P=N.S.).