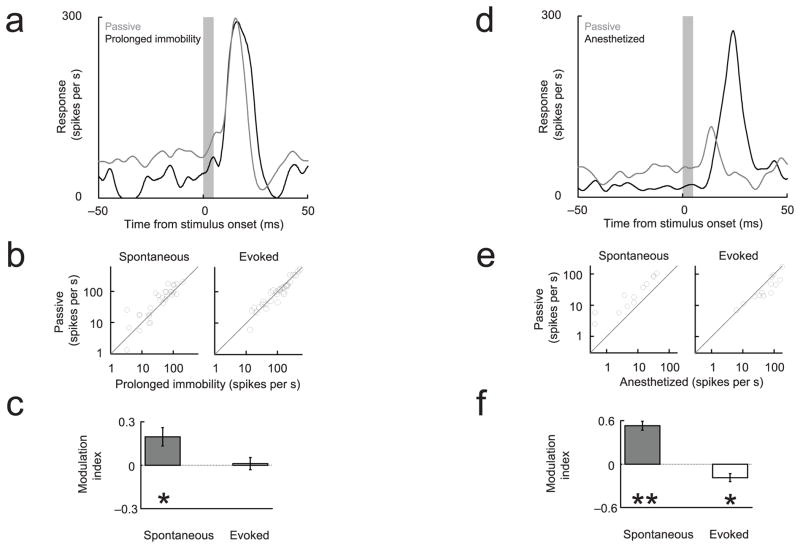
Figure 4. Changes in arousal and anesthesia have distinct neural signatures.
(a–c) Spontaneous but not evoked multiunit responses were suppressed relative to the passive condition during prolonged immobility, possibly associated with sleep. The modulation index was defined as: (Activitypassive − Activityprolonged immobility)/(Activity passive + Activityprolonged immobility). (d–f) Under light anesthesia (ketamine-medetomidine), spontaneous firing rates were also suppressed, and evoked responses were enhanced, relative to the passive condition. The modulation index was defined as: (Activitypassive − Activityanesthetized)/(Activitypassive + Activityanesthetized).